Digital Marketing vs. Data Analytics — two terms that are often confused but differ in key ways, despite some overlapping areas. In this article, you’ll learn what each field involves, how they relate to each other, and what skills you need to succeed in either career path.
To start with some context: in 2025, the global digital advertising and marketing market is estimated to be around $720 billion, with forecasts projecting growth to nearly $850 billion by 2027 (source: Wordstream). At the same time, nearly 94% of companies reported gaining measurable value from investments in professional data analytics in 2024 (source: NewVantage Partners).
A clear example of where these two fields intersect is in the use of landing pages—focused, measurable digital assets that turn marketing traffic into data-rich user actions. They highlight how creativity and analytics work together to drive performance.
Read on to discover how each discipline can support business growth—or, if you’re choosing just one, which might be the better fit for your goals.

What is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing is the use of digital channels to promote products or services to a target audience. It helps businesses reach the right people, increase brand awareness, and boost sales. By relying on data, digital marketing allows for precise targeting and message personalization, making campaigns more effective and engaging.
Common digital marketing tactics include:
- SEO – improving website rankings to attract organic traffic
- PPC Advertising – paying for ads that appear on search engines or social media
- Social Media Marketing – using platforms like Facebook and Instagram to share content and engage users
- Email Marketing – sending targeted messages to prospects or customers
- Content Marketing – creating blogs, videos, or infographics to attract audiences
- Affiliate Marketing – working with partners who promote your products for a commission
Digital marketing adapts quickly to changing market needs. Veleva and Tsvetanova (2020) define it as:
Digital strategies evolve constantly, unlike traditional campaigns, which change less often.
What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics is the process of examining raw data to find patterns, trends, and insights that support business decisions. It uses statistics, algorithms, and software tools to analyze data sets, helping organizations improve performance, streamline operations, and enhance customer experiences. In marketing, it measures campaign results and reveals areas for improvement.
Key aspects of data analytics include:
- Descriptive analytics – summarizes past data to show what happened
- Predictive analytics – uses past data to forecast future trends or behavior
- Prescriptive analytics – suggests actions based on data analysis
- Data visualization – shows data in charts or graphs for easier understanding
- Real-time analytics – analyzes data as it’s created to support quick decisions
10 Key Differences Between Digital Marketing Job and Data Analytics Job
Jobs in data analytics differ significantly from roles in digital marketing. The main contrasts lie in focus areas, required skills, daily tasks, tools, outcomes, and success metrics. Below are the key differences to help you clearly understand how these two career paths compare.
1. Primary Focus
Digital marketing focuses on promoting products or services through online channels such as search engines, social media, landing pages, email campaigns, and paid ads. The main goal is to attract, engage, and convert customers through creative content and targeted strategies.
Data analytics centers on collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data to uncover trends, generate insights, and make predictions. Analysts support decision-making across various industries by improving efficiency and performance through data.
2. Skill Sets
Digital marketers combine creative and technical skills. They create content, manage SEO/SEM, run campaigns, and use tools like Google Analytics, HubSpot, or SEMrush. They must blend creativity with data-based decisions.
Data analysts rely on technical skills such as programming (SQL, Python, R), statistical modeling, and using tools like Tableau, Power BI, and reporting software. Knowledge of machine learning or AI is useful in advanced roles.
3. Key Responsibilities
Digital marketers plan and run campaigns, create content, manage social media, perform SEO audits, and handle paid ads. They track performance metrics to improve strategies.
Data analysts interpret data, build predictive models, run statistical analyses, and create reports. Their insights support decision-making across multiple departments, not just marketing.
4. Tools Used
Digital marketers typically use:
- Google Ads – for running paid search campaigns
- Facebook Ads Manager – for social media advertising
- HubSpot – for marketing automation and customer relationship management (CRM)
- SEMrush – for SEO and competitor research
- Hootsuite – for managing social media platforms
These tools are designed specifically for marketing—used to run campaigns, manage customer interactions, and track performance.
Data analysts commonly use:
- Python – for data analysis and automation
- R – for statistical computing and data visualization
- SQL – for querying and managing databases
- Excel – for organizing and analyzing data
- Google Data Studio – for building interactive dashboards
- Tableau – for advanced data visualization and business intelligence
These tools help process large datasets, build models, and create data visualizations to present actionable insights.
5. Work Output
Digital marketers produce:
- Marketing campaigns
- Website content
- Blog posts
- Email newsletters
- Social media ads
These outputs aim to boost brand awareness, increase traffic, and drive conversions.
Data analysts deliver:
- Data models
- Reports
- Dashboards
Their work supports business decisions and may include recommendations to improve efficiency or customer targeting.
6. Measurement of Success
In digital marketing, success is measured using KPIs such as:
- Click-through rates (CTR)
- Conversion rates
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Impressions
- Engagement rates on platforms like social media or Google
In data analytics, success is measured by:
- The accuracy of predictions
- The impact of recommendations
- The ability to improve business outcomes, such as reducing costs or increasing revenue
7. Nature of Work
Digital marketing involves:
- Building creative strategies
- Developing content
- Making real-time campaign adjustments
Data analytics involves:
- Solving problems using data
- Handling large and complex datasets
- Running database queries
- Applying statistical techniques to identify trends and provide recommendations
Analysts often work across departments, not just in marketing.
8. Team Interaction
Digital marketers usually work closely with creative teams, content creators, designers, and sales to align campaigns with business goals and brand messaging. Collaboration is essential for effective content and consistent communication.
In contrast, data analysts collaborate with departments like marketing, product development, finance, and operations to deliver data-driven insights. They may also coordinate with IT to ensure proper data management and system integration.
9. Career Paths
Digital marketers and data analysts follow different career tracks, hold distinct roles, and earn significantly different salaries.
Digital marketing careers often lead to roles such as digital marketing manager, SEO specialist, social media manager, or content strategist. Some marketers move into more specialized positions like PPC expert or CRO (conversion rate optimization) specialist.
Data analytics careers progress toward roles like data scientist, business intelligence analyst, machine learning engineer, or chief data officer. As AI and big data evolve, analytics roles continue to grow in scope and demand.
10. Educational Background
Digital marketing professionals usually hold degrees in marketing, communications, business, or related fields. They often earn certifications in areas like Google Ads, SEO, or social media management.
Data analysts typically have degrees in statistics, mathematics, computer science, or economics. They may also hold certifications in data science, machine learning, or tools like Python and Tableau.
How Landing Pages Bridge Digital Marketing and Data Analytics?
Landing pages bridge digital marketing and data analytics by turning campaign traffic into measurable actions while capturing user behavior for optimization. They connect marketing efforts with real results, making it possible to track performance, test ideas, and adjust strategies based on data.
Each campaign—whether through Google Ads, email, or social media—drives users to a landing page built with one goal: conversion. Unlike general websites, landing pages are focused on actions like sign-ups, purchases, or downloads.
Their simplicity allows for clear performance tracking. Tools like Google Analytics or EventTracker by Landingi measure bounce rates, scroll depth, traffic sources, clicks, and form completions—revealing where users engage or drop off.
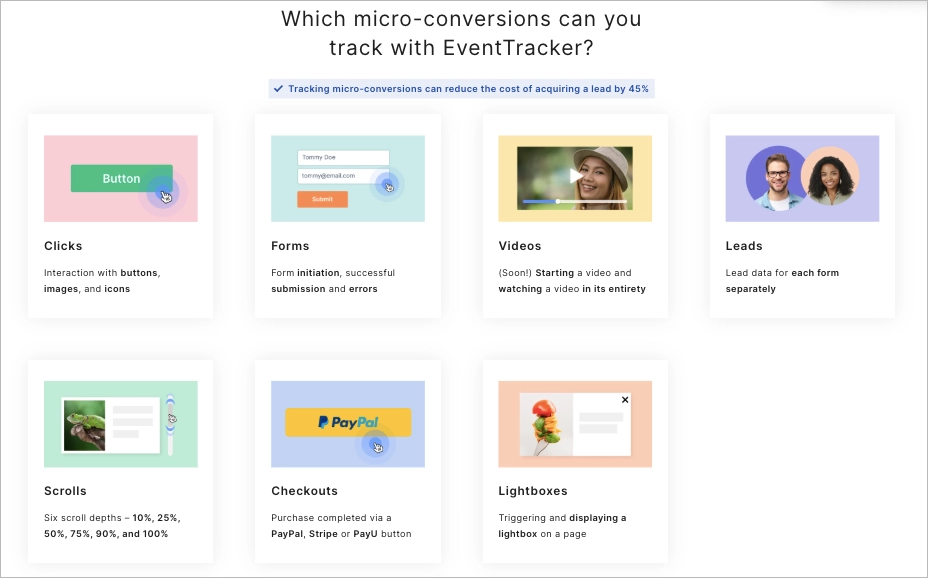
Landing pages are ideal for A/B testing. You can compare different headlines, CTAs, images, or layouts to find what works best. Some platforms even use AI to automatically direct users to the top-performing version.
These insights improve both individual campaigns and overall strategy. Marketers learn which messages convert, how audiences behave, and where to focus budget and effort.
When connected with tools like Google Ads, Meta, or CRMs, landing pages offer full-funnel visibility—from ad impression to final conversion—enabling faster optimizations and better ROI tracking.
Skills Required to Become a Data Analyst
Becoming a data analyst requires a mix of technical and analytical skills. These skills help you collect, process, and interpret large datasets effectively. Below is a list of essential skills for data analysts, along with tips on how to develop them.
1. Data Cleaning and Preparation
This involves removing errors, duplicates, or inconsistencies from raw data to ensure accuracy before analysis. Clean data is essential for generating reliable insights.
How to acquire it: Start with Google Sheets to learn basic cleaning techniques. Then move on to SQL for more advanced data preparation.
2. Statistical Knowledge
Understanding statistics helps you analyze patterns, test hypotheses, and make data-driven conclusions.
How to acquire it: Take beginner-friendly courses on platforms like Khan Academy. Practice using real datasets in Excel or R.
3. Programming Skills
Languages like Python, R, and SQL are essential for data manipulation, analysis, and automation. Python is widely used for its simplicity and flexibility; SQL is key for working with databases.
How to acquire it: Start with Python due to its beginner-friendly syntax. Use platforms like Codecademy or Coursera for hands-on practice.
4. Data Visualization
Creating clear visualizations helps communicate insights to stakeholders and makes complex data easier to understand.
How to acquire it: Start with tools like Google Data Studio or Tableau Public. Learn key chart types and when to use them for different types of data.
5. Excel Mastery
Excel is a core tool for data analysis, offering features like pivot tables, VLOOKUP, and data summarization.
How to acquire it: Take focused Excel courses on platforms like Udemy. Practice advanced tools such as pivot tables, macros, and nested formulas.
6. Problem-Solving
Data analysts need a problem-solving mindset to identify trends, spot outliers, and extract actionable insights from data.
How to acquire it: Join online challenges on platforms like Kaggle to practice solving real-world data problems and sharpen your analytical thinking.
Skills Required to Become a Digital Marketer
To succeed in digital marketing, you need a mix of technical, analytical, and creative skills. These help you engage audiences, manage platforms, and improve campaign results. Below is a list of key digital marketing skills, along with tips on how to develop each one.
1. SEO and SEM Knowledge
Understanding SEO and SEM is key to increasing website visibility and attracting traffic through search engines.
Pro-tip: Use free tools like Google Search Console and SEMrush to practice keyword research and on-page SEO techniques.
2. Content Marketing
Creating valuable content helps attract and retain customers, making it a core skill in digital marketing.
Pro-tip: Start a blog or write on platforms like Medium. Try different content types—articles, videos, infographics—and track performance in Google Analytics (page views, bounce rate, time on page).
3. Social Media Marketing
Managing social media platforms is essential for building brand awareness and engaging with audiences.
Pro-tip: Use tools like Hootsuite to schedule posts and track performance. Gain hands-on experience by managing a personal or small business account.
4. Data Analytics
Analyzing campaign data helps marketers optimize strategies, track ROI, and focus efforts on what works.
Pro-tip: Take Google Analytics Academy courses to learn how to track key metrics like engagement and conversions. Practice reading and interpreting reports.
5. Email Marketing
Email is a powerful channel for direct communication and customer retention. Crafting effective campaigns is a key skill for digital marketers.
Pro-tip: Subscribe to newsletters and study their structure. Use free tools like Mailchimp to practice creating and sending campaigns.
6. PPC Advertising
Pay-per-click (PPC) ads, such as Google Ads, are essential for driving targeted traffic and generating leads in digital marketing.
Pro-tip: Take Google Ads’ free certification course to learn PPC fundamentals. Run small-budget campaigns to understand bidding, targeting, and conversions.
If you’re looking to quickly build practical skills and gain domain knowledge in digital marketing, explore our article on the best professional courses available.
In addition to mastering specific digital marketing areas, it’s important to build general skills that support long-term success:
- Creativity – generating original ideas and engaging content
- Communication – delivering clear and persuasive messages
- Adaptability – adjusting quickly to new tools and trends
- Technical proficiency – navigating marketing and analytics platforms
- Project management – organizing campaigns to meet goals and deadlines
- Customer focus – tailoring strategies to audience needs
- Proactivity – anticipating opportunities and acting ahead of time
What is the Future of Digital Marketing?
The future of digital marketing will be shaped by advances in AI, personalization, and immersive experiences. As consumers expect more tailored and engaging content, marketers will need to adopt cutting-edge technologies to stay competitive. Key trends on the horizon include:
- AI-Driven Automation: AI will continue to power real-time decision-making, customer experience optimization, and predictive marketing.
- Hyper-Personalization: Brands will use data to tailor messages and offers based on individual preferences and behaviors.
- Voice Search Optimization: With smart devices like Alexa and Google Assistant, voice search will become a critical focus.
- Interactive and Video Content: Video will remain dominant, joined by polls, quizzes, AR experiences, and social media formats like stories and reels.
- Omnichannel Integration: Seamless customer experiences across apps, websites, social media, and email will become essential.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Marketing
Several new technologies are expected to transform the digital marketing landscape:
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Unlike today’s task-specific AI, AGI would allow machines to think and solve problems across multiple contexts. This could lead to AI-driven content creation with human-like creativity.
- Quantum AI: By combining AI with quantum computing, marketers could process massive datasets instantly, leading to faster insights, more precise targeting, and highly personalized campaigns.
- AI and Energy Efficiency: As AI demands grow, companies like Google and Amazon are investing in nuclear power to run data centers sustainably. This shift may improve the performance and reliability of large-scale marketing platforms.
Privacy, Compliance, and Ethics
Evolving data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA are forcing marketers to move away from third-party cookies. First-party data collection and transparent consent practices will become the norm, requiring a shift toward trust-based personalization.
New Roles and Specializations
As digital marketing grows more complex, new roles will emerge:
- AI Marketing Specialist – focuses on machine learning–driven campaigns
- Data Privacy Officer – ensures compliance with privacy regulations
- Sustainability Marketer – integrates environmental responsibility into brand strategy
- Ethical AI Strategist – manages the responsible use of AI in marketing
What is the Future of Data Analytics?
The future of data analytics will be shaped by AI, real-time processing, and broader access to analytical tools. As the global data volume grows—expected to reach 175 zettabytes by 2025 (IDC)—organizations will depend more on advanced analytics to extract insights quickly and accurately. AI and machine learning will automate much of the analysis, helping businesses process complex datasets faster and make better decisions with less manual effort.
Predictive and prescriptive analytics will become more common, allowing companies to anticipate outcomes and take action before problems arise. Gartner predicts that by 2026, over 70% of businesses will rely on these methods to move from reactive to proactive decision-making, gaining a competitive edge through speed and precision.
Another major trend is the democratization of analytics. As tools like Microsoft Power BI and Tableau become easier to use, employees across departments—not just data scientists—will be able to explore data and make informed decisions. This shift will embed data-driven thinking into everyday business operations and expand the role of analytics far beyond IT and analytics teams.
Optimize Every Marketing Touchpoint with Data-Driven Landing Pages
If you’re ready to gain hands-on experience with digital marketing and data analytics, try Landingi—a powerful yet user-friendly platform designed for:
- Creating landing pages, pop-ups, lightboxes and other digital assets,
- Using AI tools to generate content and optimize SEO
- Automating multilingual translations and building programmatic pages for easy market expansion
- Running A/B tests and using EventTracker to collect and analyze marketing data
- And much more
Start a free trial or use the forever free plan to begin your digital marketing journey. Build landing pages, add targeted content, run A/B tests to find top-performing versions, and analyze results to improve performance. This end-to-end process shows how digital marketing and data analytics can work together to drive better outcomes for your campaigns.






