Entity-based SEO flips the script on traditional search engine optimization. Instead of chasing keywords, you’re optimizing for meaning — helping search engines like Google understand the things your content is about. Why? Because modern algorithms care more about context than spelling. They want to know what something is, not just how it’s typed.
An entity in SEO is anything specific and identifiable: a person, place, brand, or concept — think “banana bread,” “SEO,” or “Statue of Liberty.” Google connects these dots using its Knowledge Graph, which has fueled entity-based search since 2012. That’s how it knows whether “Apple” means fruit or iPhone, based on user intent.
And it’s getting sharper by the second — Google’s Knowledge Graph now handles over 800 billion facts about 8 billion entities, making entity-based SEO fundamental for ranking well in 2025.
When you clarify which entities your content covers, you help search engines recognize its meaning, rank it higher for relevant search queries, and even sharpen your local entity SEO.
In this post, we’ll show you how to find your key entities, map their relationships, and roll out entity-based SEO across your content — from schema markup to internal links. Let’s get into it.

What Is Entity-Based SEO?
Entity-based SEO is a search engine optimization strategy that centers content around entities—concrete, unique things like brands, people, places, or concepts—rather than isolated keywords. This approach aligns with how search engines understand meaning today: through the context, connections, and relationships between entities in Google’s Knowledge Graph.
Let’s do some practice.
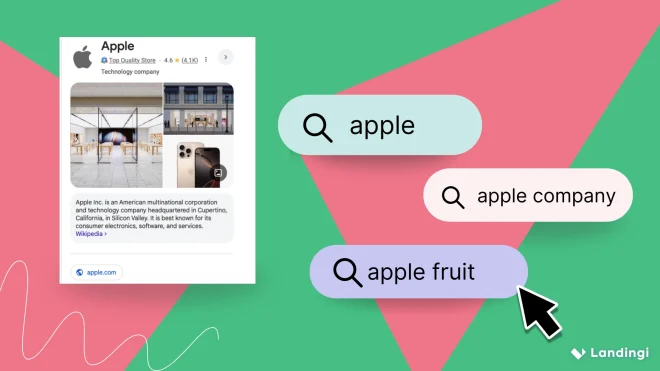
Imagine you’re writing about Apple. Are we talking fruit or tech? Google won’t guess—it will analyze related entities in your content to decide.
Mention “company”, “iPhone,” “Tim Cook,” or “Silicon Valley,” and it knows you mean Apple Inc.:
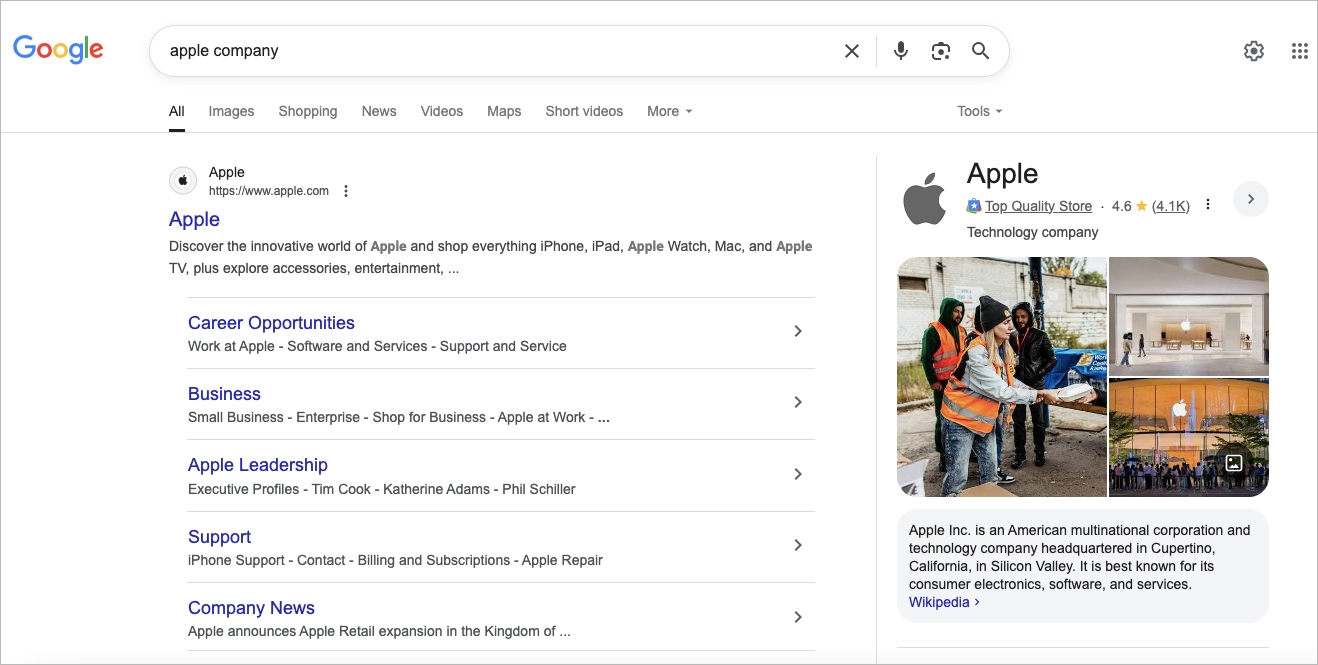
Mention “baking,” “fiber,” or “fruit salad,” and it swings the other way:
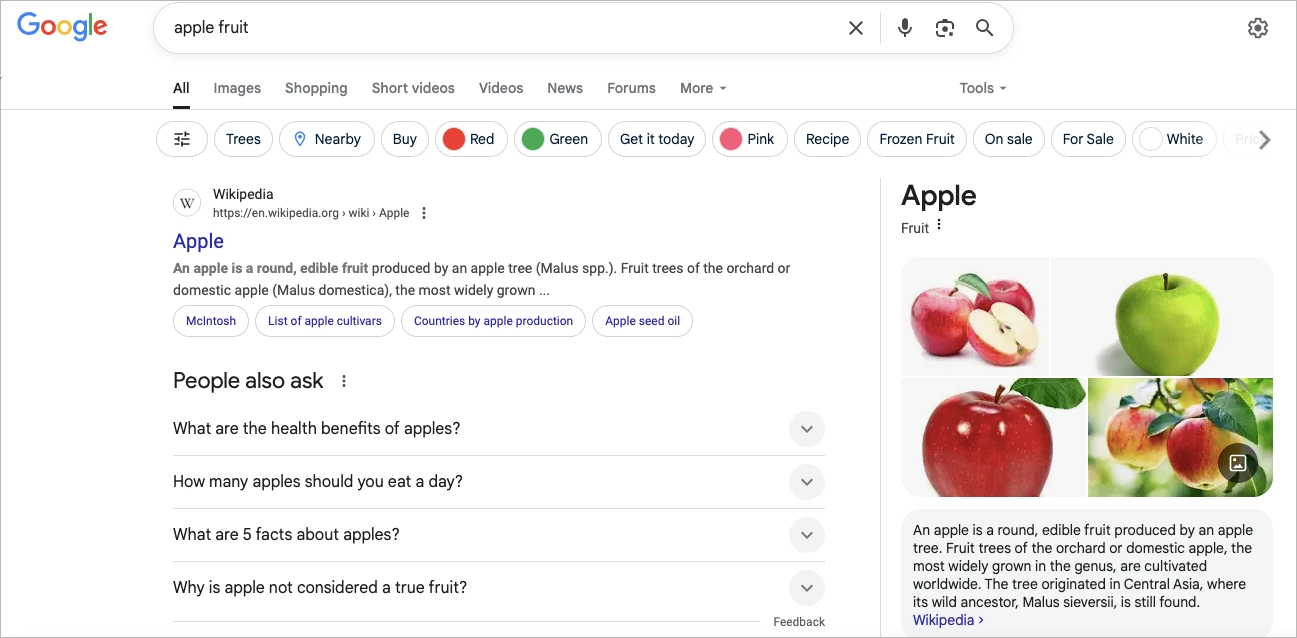
That’s entity recognition at work—and it’s what fuels modern search relevance.
Entity SEO zooms out and asks: what’s the topic really about? Then it zooms back in, mapping specific entities, adding structure with schema markup, and reinforcing context with internal links and co-mentioned related entities.
Implementing entity-based SEO gives your content staying power: better user engagement, richer search snippets, stronger search rankings, and more relevant search queries matched to your content—because it actually understands what you’re saying.
What’s the Importance of Entity-Based SEO?
Entity-based SEO is important because it mirrors how Google actually understands content today—through entities and their relationships, not just strings of keywords. This approach improves how search engines interpret your pages, helping them connect your content to the right topics, queries, and audiences with far greater precision.
Users don’t search like they used to. They ask questions, use voice, expect Google to understand what they mean—not just what they type. And Google delivers, thanks to entity recognition, the Knowledge Graph, and semantic search algorithms like BERT and MUM. If your content doesn’t speak this language, it won’t show up where it should.
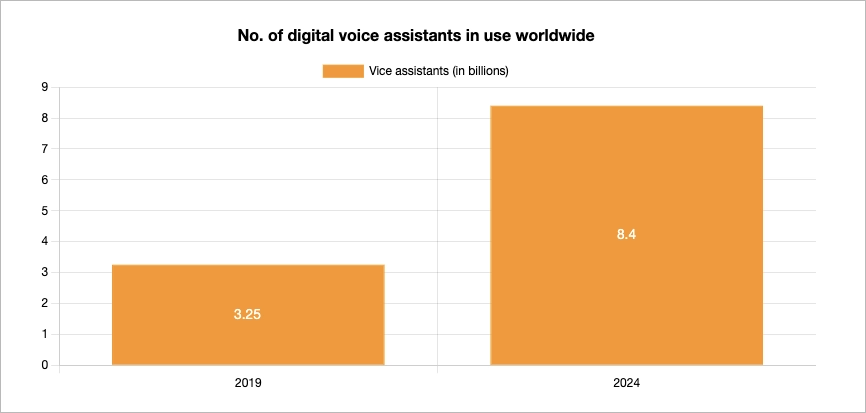
By optimizing for entities—mentioning related concepts, adding context, using schema markup, and clarifying relationships—you increase your chances of appearing in rich results, Knowledge Panels, and featured snippets. You also create content that’s more comprehensive and user-friendly, which boosts engagement, reduces bounce, and strengthens your authority.
For businesses, this translates to more accurate visibility, stronger brand recognition, and better alignment with how search engines actually work. Especially in competitive spaces or local entity SEO, it’s what gives your content the edge to rise above keyword-only strategies. If you want search engines to truly “get” you, entity-based SEO is how you make that happen.
Dominate SERPs with AI Landing Pages that understand context and boost authority, not just keywords.
How Does Entity-Based SEO Work?
Entity-based SEO works by showing search engines exactly which people, places, brands, or concepts your content refers to—then linking those entities to others in Google’s knowledge network. Instead of matching keywords, you’re helping search engines understand the real-world meaning behind the words on your page.
Think of it like setting the table for Google: you’re not just serving words, you’re plating context, connections, and clarity.
Here’s what that process looks like in real life—say you’re writing about Tesla (the company, not the inventor):
Step 1: Identify key entities
You don’t just focus on “Tesla.” You map related entities like Elon Musk, Model Y, electric vehicles, Gigafactory, and Autopilot. These signal relevance.
Step 2: Connect the dots
Using tools like InLinks, you create a content map that shows how these entities link together. Elon Musk leads Tesla. Model Y is a product. The Gigafactory is where it’s built. This internal map guides how you organize content and link concepts, adding structure and depth that search engines can recognize.
Here’s a quick video that shows how to create a topical map using InLinks.
Step 3: Write content with context
Don’t just name-drop. Explain what the Model Y is, why it matters, how it compares to other EVs, and how it fits into Tesla’s mission. This turns an article into a search engine-friendly knowledge hub.
Step 4: Mark it up
Use schema markup to label Tesla as an Organization, Model Y as a Product, Elon Musk as a Person. This structured data helps search engines understand entities and their attributes, which boosts your odds of showing in rich snippets and Knowledge Panels.
Step 5: Internally link with intent
Every mention of “Model Y” should link to your dedicated Model Y page. Mention “electric vehicles”? Link to your broader EV guide. This reinforces entity relationships and improves crawlability.
Step 6: Keep it fresh
If Tesla launches a new model or Elon Musk makes headlines (again), update your content to reflect that. Entities evolve—your content should too.
Entity-based SEO isn’t about stuffing terms—it’s about showing how entities relate, giving search engines the context they need to rank your content where it belongs. When done right, it tells Google: “This page gets it”—and Google rewards that with visibility, relevance, and reach.
Craft landing pages that map directly to entities Google understands—with Landingi’s Builder.
What Is the Difference Between Entity and Keyword SEO?
The difference between entity-based SEO and keyword SEO lies in what search engines are actually trying to understand: surface-level words or deeper meaning. Keyword SEO focuses on matching specific phrases. Entity SEO focuses on identifying what those phrases represent—and how they connect.
Here’s how it plays out.
Let’s say someone searches for “jaguar.” Keyword SEO treats it as a string of characters—so it might serve up pages about the big cat, the British car brand, or even a sports team, depending on what’s optimized best for that term.
Entity-based SEO, though, digs into context. If your page mentions “luxury cars,” “electric SUVs,” and “Jaguar Land Rover,” Google understands that your content is about the automotive brand, not the jungle predator. It’s reading between the lines—using entity recognition and semantic understanding to disambiguate and deliver what the user actually meant.
Keywords are input signals. They tell Google what users typed. But entities tell Google what users want. That distinction matters, especially now that Google’s algorithms—fueled by BERT, MUM, and the Knowledge Graph—prioritize relevance, context, and meaning over simple keyword density.
How to Improve Google Ranking With Entity-Based SEO?
To improve your Google ranking with entity-based SEO, you need to optimize not just for words—but for meaning, context, and the relationships between identifiable things Google understands as entities.
Here’s how to turn your content into something search engines don’t just crawl—but actually get.
1. Identify relevant entities (not just keywords)
Don’t build content around “travel tips.” Build it around recognizable entities: JetBlue, EU roaming charges, TripIt, TSA PreCheck. Use tools like InLinks or Google’s NLP API to find entities that match what people actually search for—not just the phrases they use.
2. Cover entities like a subject-matter expert
If you’re writing about the Samsung Galaxy Watch 6, don’t stop at the name. Reference Wear OS 4, Apple Watch Series 9, BioActive Sensor, blood pressure monitoring. This kind of depth signals topical authority—and Google’s algorithms notice.
3. Use structured data to define entities clearly
Mark up content using schema.org—especially for people, places, products, and organizations. If you’re writing about Marie Curie, use the Person schema and include her professions, Nobel Prizes, and affiliations. This makes it easier for Google to connect the dots in the Knowledge Graph.
Build SEO-smart pages that reflect intent, rank better, and convert faster with Landingi.
4. Build internal links that reflect real-world relationships
Link intelligently: your article on blockchain should point to smart contracts, Ethereum, and decentralized finance. These aren’t just SEO hacks—they mirror actual entity relationships that reinforce your site’s topical relevance.
5. Align with E-E-A-T by referencing authoritative entities
Don’t just claim expertise—demonstrate it by citing entities like Mayo Clinic, PubMed, or Dr. Rhonda Patrick when writing about health. Google sees these associations and interprets them as credibility signals.
6. Keep entity references accurate and up to date
Still calling Meta “Facebook” in a current-year article? That’s a red flag for outdated content. If you mention company names, CEOs, tools, or legislation—make sure it reflects the latest data Google expects to see.
7. Audit your entity coverage with NLP tools
Run your content through tools like InLinks or Google’s NLP API to see which entities are detected—and which are missing. For example, if you’re targeting “sustainable fashion” but not mentioning carbon footprint or Fair Trade Certified, it’s time to fill the semantic gaps.
FAQ About Entity-Based SEO
Below are website owners’ most common questions when trying to understand, implement, or improve entity-based SEO.
Where to Find Entity SEO Checker?
You can find an entity SEO checker in tools like InLinks, SEO.ai, Sitechecker, Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Google Search Console—platforms built to help you optimize content based on entities and their relationships. InLinks stands out for its entity-first internal linking and topic mapping, while SEO.ai adds AI-driven content optimization. Sitechecker combines on-page SEO with entity insights, and although Ahrefs and SEMrush are keyword-heavy, they both support semantic search analysis. Even Google Search Console, while not dedicated to entity SEO, provides valuable data on how search engines recognize your content.
How Entities Work in Search Algorithms?
Entities help search engines shift from keyword matching to understanding meaning. When someone types a query, Google doesn’t just scan for words—it looks for known entities and how they relate.
Let’s say a page mentions “World Cup,” “Mbappé,” and “penalty shootout.” Google connects these as related entities, understands the topic is football (not cricket), and delivers results with high contextual relevance.
Behind the scenes, it pulls from the Knowledge Graph, analyzes entity relationships, and uses models like BERT to interpret user intent. If your content makes those connections clear—with smart linking, structured data, and relevant entities—you’re speaking Google’s language.
What Are the Best Tools for Entity-Based SEO?
The best tools for entity-based SEO include InLinks, SEO.ai, Ahrefs, SEMrush, Clearscope, Surfer SEO, Schemantra, and Google Search Console—each tackling a different piece of the entity puzzle. These platforms help you identify relevant entities, optimize content semantically, apply structured data, and monitor how search engines interpret your site. InLinks is unmatched for internal linking and entity planning, while SEO.ai brings AI-driven clarity to content creation. Combine these with Clearscope, Surfer, or Schemantra, and you’ve got a toolkit built for ranking web content through real context and meaning.
| Tool | Key Use | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| InLinks | Entity mapping, internal linking | Full entity SEO execution |
| SEO.ai | AI-based entity discovery | Smarter content creation |
| Ahrefs / SEMrush | Semantic + competitor analysis | Scaling and refining entity strategy |
| Clearscope / Surfer | Semantic content optimization | Deepening contextual relevance |
| Schemantra | Schema markup for entities | Structured data and rich results |
| Google Search Console | Entity visibility and query tracking | Measuring real-world performance |
How Entities Connect to Google’s Knowledge Graph?
Entities connect to Google’s Knowledge Graph through structured data, contextual signals, and consistent mentions across trusted sources.When Google identifies an entity—say, a person, brand, or concept—it checks if it’s unique, notable, and well-defined enough to add to its Knowledge Graph.
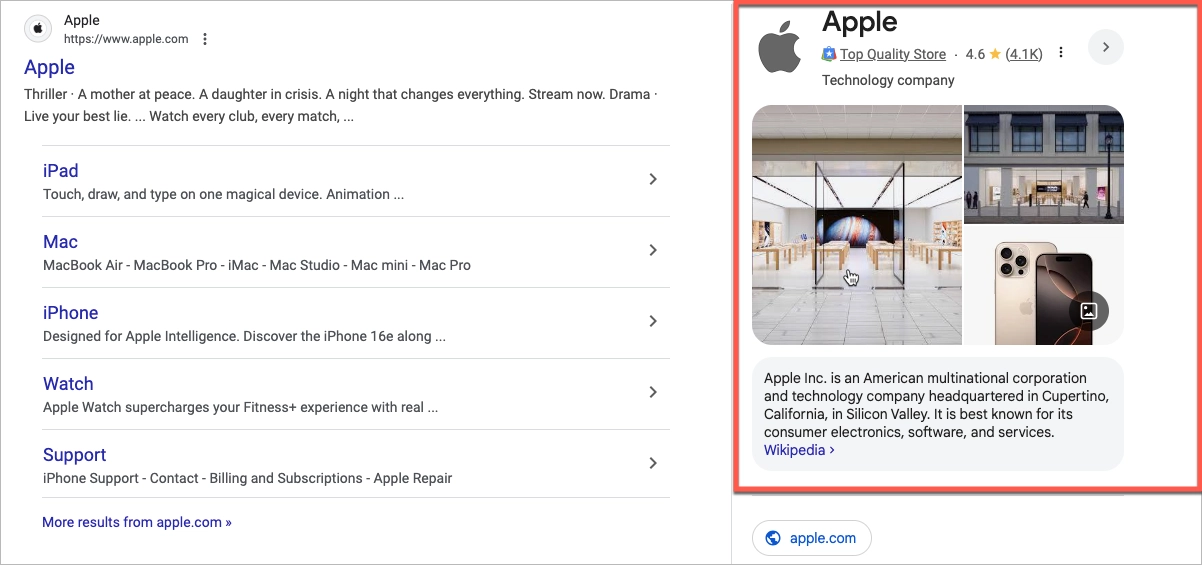
Let’s say your business is mentioned on your website, listed on Google Business Profile, and referenced in relevant directories using the same name, description, and schema. Google links those signals to recognize it as a primary entity, then relates it to other entities—like your industry, founder, or location.
Once added, your entity can power Knowledge Panels, enhance search results, and influence how search engines understand your brand’s authority and relationships.
What Are Entity Relationships and Contextual Relevance in SERPs?
Entity relationships and contextual relevance in SERPs refer to how Google understands connections between entities and uses them to serve more accurate, meaningful search results.
For example, if a page mentions “Adobe,” “Photoshop,” and “digital design,” Google sees these as related entities. It understands that Photoshop is a product of Adobe and connects them through the context of creative software—boosting the page’s visibility for relevant queries, even if the keyword “graphic design tool” isn’t explicitly used.
These entity relationships—like brand-product, person-organization, or concept-subtopic—help Google deliver results that better match user intent. The stronger the contextual relevance between entities mentioned, the more likely your content ranks for semantic search queries.
Start a free trial and create landing pages that turn context into conversions.
Understand Entity-Based SEO to Boost Landing Page Traffic
To boost your landing page traffic in 2025, you need more than good copy—you need smart context. And that’s exactly what entity-based SEO delivers. It’s not just a shift in strategy; it’s a shift in how search engines like Google process and rank your content.
By focusing on entity optimization, you help Google connect your content with real-world entities in its Knowledge Graph, better match it to relevant search queries, and increase your chances of ranking in both national and local entity SEO results.
Well-structured landing pages can act as high-conversion, entity-rich hubs. They allow you to target specific topics, products, or audience segments with precision — and with proper schema and internal linking, they reinforce your site’s topical authority.
Ready to turn your SEO traffic into conversions? Build a high-converting landing page that matches search intent and drives real results with Landingi.