The history of SEO began in mid-1990s, when digital marketers started optimizing websites to appear higher in search engine results—but its roots reach back even earlier, to the chaotic early days of the internet.
Search engine optimization didn’t start as a formal practice. Before the term even existed, marketers and webmasters in the mid-1990s were already trying to influence search rankings by tweaking meta tags and keyword usage. But the turning point came in 1997, when the phrase “search engine optimization” first surfaced. Pioneers like John Audette and Bruce Clay began shaping what would eventually become one of the most influential marketing disciplines online.
Today, SEO is an $86.8+ billion industry (as of 2025, according to Statista) constantly adapting to changes in technology, user behavior, and Google’s algorithm updates. But how did we get from stuffing keywords into meta tags to optimizing for AI-powered search engines?
To fully understand the evolution of SEO, let’s break it down by key phases.

When Did SEO Become Popular?
SEO became popular in the early 2000s, when Google’s rise—and its unexpected alliance with Yahoo—turned a nerdy, behind-the-scenes practice into a must-have marketing strategy.
Back in the mid-1990s, what we now call SEO looked more like a digital Wild West. There were no rules, no standards, and definitely no algorithm updates. Marketers used terms like “web positioning” or “site promotion” instead. If you knew how to tweak meta keywords or get listed in Yahoo’s directory, you were already ahead of the game. But it wasn’t exactly mainstream. Most business owners had no idea that getting found online could be influenced—let alone strategically planned.
Then, in 1997, the phrase “search engine optimization” started popping up in agency decks and conference talks. It wasn’t common knowledge yet, but the seed was planted.
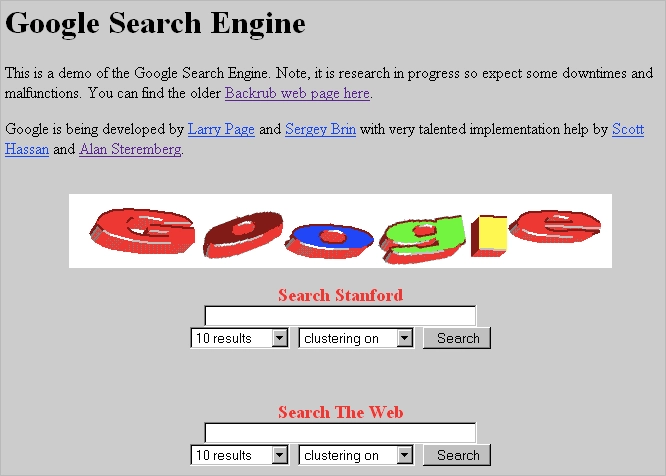
That seed exploded a year later, when Google quietly entered the scene with something no other engine had: PageRank. It is an algorithm used by Google Search to rank web pages in its search engine results. So, instead of counting how many times a keyword appeared, Google looked at how many quality sites linked to yours. Suddenly, content and links mattered more than stuffing keywords into invisible tags.
Still, Google was the underdog. The real turning point came in 2000, when Yahoo—then the king of portals—chose Google to power its search results. Overnight, millions of users were unknowingly using Google’s algorithm every time they typed into Yahoo’s search bar. Every search result had a tiny caption: “Powered by Google.” That line changed a lot.
Between 2000 and 2005, businesses caught on. Suddenly, being on the first page wasn’t a technical curiosity—it was essential to getting customers. Link building became an industry. PPC ads appeared. Agencies sprang up offering “ranking guarantees.”
Then, in 2003, Google launched the infamous Florida update, nuking spammy tactics and forcing marketers to clean up their act. Ethical SEO became the new standard.
Back in ‘97, SEO was manual—now launch hundreds of landing pages with Programmatic Pages.
Who Invented SEO?
The invention of search engine optimization is often credited to early digital marketers like Bob Heyman, Leland Harden, Danny Sullivan, and Bruce Clay—figures who, in the mid-to-late 1990s, began testing how early search engines ranked web pages, and how those rankings could be improved using keywords, links, and metadata.

Let’s rewind to 1995. The world wide web was still new territory, and search engines like Excite or Lycos were just learning how to crawl and catalog websites. Most people didn’t think much about search rankings—until, legend has it, a certain rock band’s manager couldn’t find their site online.
That band was Jefferson Starship.
According to a widely shared anecdote, Bob Heyman and his partner Leland Harden, working on the band’s digital promotion, realized that the site would show up higher if the band’s name appeared more often on the page. So they added more mentions. That simple move—essentially early keyword stuffing—helped the site climb in search engine results. It wasn’t called SEO yet, but that moment is often cited as one of its earliest sparks.
Then, in 1997, a small agency called Webstep Marketing dropped a phrase that would change online marketing forever: “search engine optimization” (though some sources credit journalist Danny Sullivan with helping to popularize the term around the same time). It appeared in a pitch deck, giving a name to what was quickly becoming a strategy.
Not long after, Sullivan launched Search Engine Watch—a blog that became a bible for webmasters trying to make sense of meta tags, inbound links, and the mysterious logic behind search engine results pages.
If Danny taught the theory, Bruce Clay brought the practice. One of the first people to offer SEO services professionally, Clay helped shift SEO from hobbyist tinkering into a full-blown industry. He trained marketers, wrote guides, and even coined terminology that still shapes how the SEO strategy world talks today.
Generate AI‑powered landing pages in seconds with AI Landing Pages — smarter content, faster leads.
5 Key Phases of SEO Evolution From Its Inception to 2025
The history of SEO reads like a fast-paced tech saga—from stuffing keywords into meta tags in the ’90s to optimizing for AI-driven conversational search in 2025. Every phase in this evolution has been shaped by changes in search engine technology, Google’s algorithm updates, and how people use the internet to find relevant content.
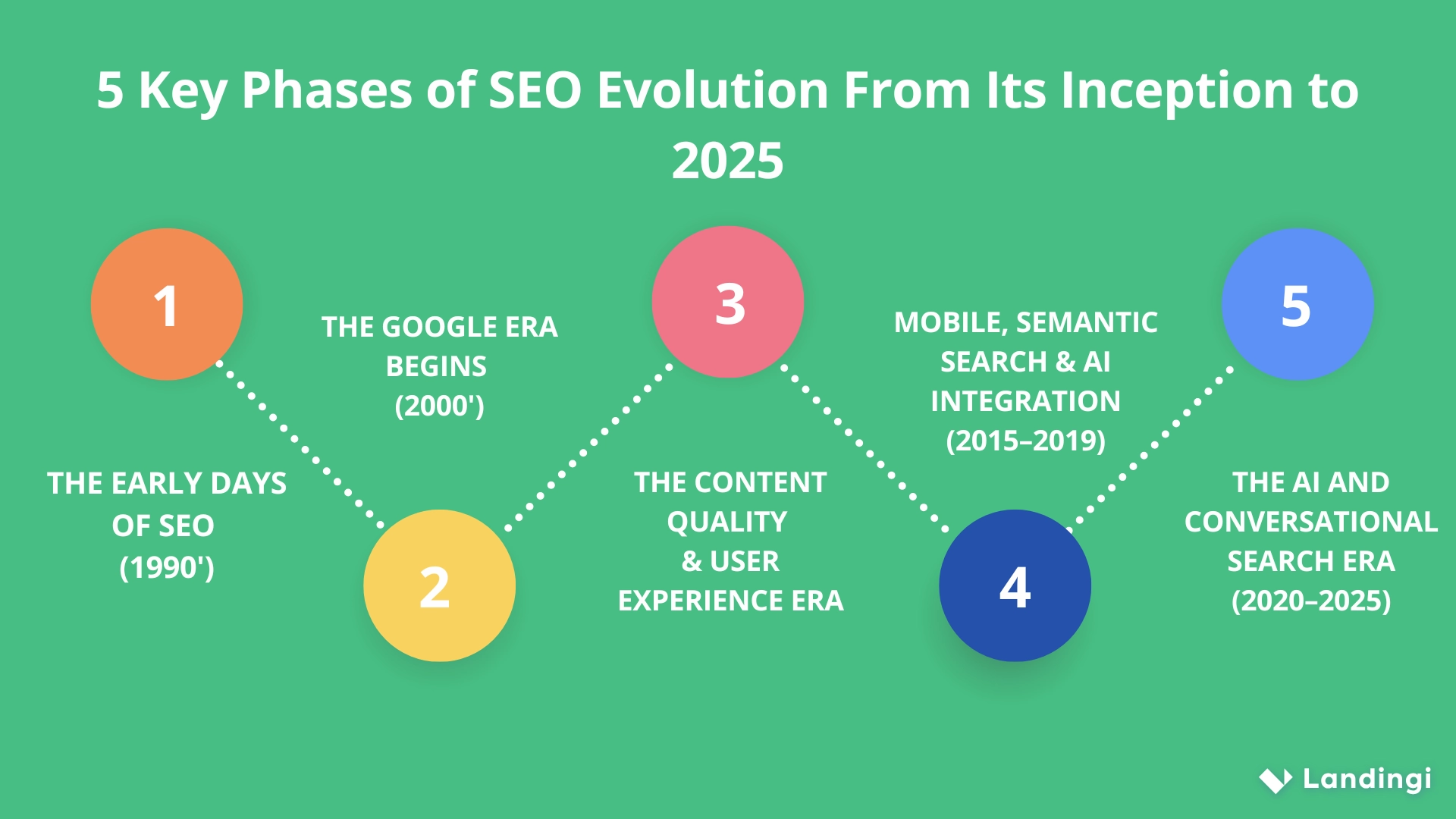
1. The Early Days of SEO (1990s)
The SEO story began in the 1990s, when the first search engines like AltaVista, Lycos, and Yahoo Directory tried to make sense of the growing world wide web. Back then, just including the right keywords in your meta tags and submitting your site to a directory could push you to the top of search engine results pages.
There were no SEO tools, no guidelines—just trial and error. Webmasters relied on keyword stuffing, and no one talked about user intent or inbound link relevancy. But by 1997, the term “search engine optimization” had started popping up, giving this underground practice a name—and a future.
What changed in this phase:
- Semantic SEO: Practically nonexistent; search engines matched keywords literally without understanding context.
- On-Site SEO: Focused entirely on keyword stuffing in meta tags and visible content.
- Off-Site SEO: Minimal to no emphasis—directory listings were the closest thing.
- Local SEO: Not a defined concept yet; directories like Yahoo! listed sites by category, not location.
- Technical SEO: Manual site submissions were key; no sitemaps or crawl control mechanisms existed.
2. The Google Era Begins (2000s)
Everything changed when Google launched in 1998. By the early 2000s, it had become the dominant search property, thanks in large part to its PageRank algorithm, which made external links a key ranking factor. This ushered in the first real wave of SEO strategy, where off-page factors like backlinks became just as important as what was on the page.
Google’s Florida update in 2003 marked a crackdown on black hat SEO tactics and keyword stuffing. Suddenly, quality content and ethical optimization mattered. The SEO industry began to professionalize—agencies were formed, paid search ads took off, and tools like Google Analytics and Webmaster Tools gave marketers the data to make smarter decisions.
What changed in this phase:
- Semantic SEO: Google’s PageRank laid the groundwork for interpreting authority via backlinks, not context yet.
- On-Site SEO: Content quality and structure became more important, though keywords still dominated.
- Off-Site SEO: Backlinks became a major ranking factor—link building became essential.
- Local SEO: Began to emerge with early iterations of Google Maps and business listings (e.g., Google Local in 2004).
- Technical SEO: Google Webmaster Tools (2006) introduced crawl error reports, sitemaps, and robots.txt feedback.
3. The Content Quality & User Experience Era (2010–2014)
As the internet matured, Google shifted its focus toward delivering high-quality, relevant search results. The Panda update (2011) penalized sites with thin or duplicate content, and Penguin (2012) targeted spammy link-building tactics. SEO was no longer about gaming the system—it was about creating high-quality content that deserved to rank.
Google also started prioritizing user experience. By 2010, site speed became a ranking factor. By 2014, mobile-friendly web pages were favored in search rankings, a signal of what was to come with mobile-first indexing. This era taught marketers that content had to serve real users, not just search engine crawlers.
What changed in this phase:
- Semantic SEO: Still limited, but Panda and Penguin encouraged relevance and content quality.
- On-Site SEO: User-focused design, better content structure, mobile-friendly formatting started to impact rankings.
- Off-Site SEO: Spammy link-building penalized; natural, high-quality links became the goal.
- Local SEO: Google My Business launched in 2014, standardizing local listings and map pack visibility.
- Technical SEO: Site speed became a ranking factor (2010), mobile usability and crawlability were prioritized.
4. Mobile, Semantic Search & AI Integration (2015–2019)
The second half of the 2010s brought some of the biggest shifts in SEO history. Mobile search overtook desktop, and Google responded with Mobilegeddon in 2015, giving a boost to mobile-friendly content in mobile search results.
But the real revolution came with semantic search and AI. Google’s Hummingbird update (2013) allowed the algorithm to understand conversational search and natural language. RankBrain (2015), a machine-learning system, helped interpret ambiguous user queries. And by 2019, BERT allowed Google to grasp the nuance behind words and phrases, dramatically improving how it understood search intent.
SEO professionals had to think beyond keywords—now it was about context, relevance, and optimizing for how people actually talk and search.
What changed in this phase:
- Semantic SEO: Major shift—Hummingbird (2013), RankBrain (2015), and BERT (2019) enabled true context-based understanding.
- On-Site SEO: Focus moved to natural language, search intent, and structured content aligned with user queries.
- Off-Site SEO: Quality of backlinks continued to matter, but context (relevance of linking domain) gained weight.
- Local SEO: Mobile search dominance emphasized proximity-based results; local citations and reviews gained value.
- Technical SEO: Mobile-first indexing (2016+), structured data (Schema.org), HTTPS adoption, and crawl budget optimization became key.
5. The AI and Conversational Search Era (2020–2025)
In the 2020s, artificial intelligence took over both sides of the search equation—how engines rank content and how users search. By 2020, BERT was integrated into nearly all English queries. Google’s web crawler was understanding more than words; it was reading meaning.
At the same time, voice search became mainstream thanks to assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. People were asking questions out loud, triggering conversational search. Content had to be optimized for full sentences, spoken questions, and natural answers.
Then came the tipping point: ChatGPT launched in late 2022, and by 2023, millions of users were turning to AI for search-like tasks. Search engines had to respond. Microsoft Bing integrated GPT-4, Google launched Bard, and Google announced Gemini—its most advanced generative AI, now shaping search engine results with AI Overviews and personalized responses.
In this AI-powered era, SEO means more than creating content—it means proving your content is real, expert-driven, and trustworthy. Google emphasizes E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness), especially in a world flooded with AI-generated fluff.

What changed in this phase:
- Semantic SEO: AI models like BERT, MUM, and Gemini allow for near-human understanding of nuance, tone, and search intent.
- On-Site SEO: Content must sound natural, answer complex questions, and demonstrate E-E-A-T—especially in AI-generated contexts.
- Off-Site SEO: Link quality remains important, but brand mentions, topical authority, and author transparency are also evaluated.
- Local SEO: Voice search and mobile behavior shape local queries; AI can infer local intent even without location terms.
- Technical SEO: AI crawlers analyze page meaning, not just structure; Core Web Vitals, structured data, and mobile UX remain critical for visibility.
| Phase | What Defined It |
|---|---|
| 1990s | Meta tags, keyword stuffing, directories |
| 2000–2009 | PageRank, backlinks, Google Analytics, paid search |
| 2010–2014 | Panda, Penguin, mobile-friendly updates |
| 2015–2019 | RankBrain, BERT, mobile-first indexing, semantic search |
| 2020–2025 | Generative AI, conversational search, voice optimization |
How AI Changed SEO?
AI changed SEO by helping search engines better understand what people really mean when they search—focusing more on intent and context than just matching keywords.
From 2020 to 2025, artificial intelligence has transformed the search engine optimization playbook, redefining everything from how search engines read content to how marketers write it.
Search used to be predictable: type a query, scan the list of 10 blue links, click, scroll, repeat. But as AI became the engine behind Google’s algorithm, the entire search experience evolved.
Here’s how AI has changed the way we optimize for search:
AI Understands Search Intent and Context
At the heart of this shift is a deeper understanding of user queries. Google’s BERT and MUM models introduced natural language processing that allowed the algorithm to go beyond exact matches and parse nuance. Instead of matching keywords, Google’s search now analyzes context—what the user really wants, not just what they typed.
This has massive implications for SEO strategy. Content has to answer real questions, provide relevant content, and align with search intent. Pages that focus on creating high quality content—not just targeting keywords—are the ones that win in search engine rankings.
AI-Driven Content Creation and Optimization
On the marketer’s side, AI has become a co-writer. Tools like ChatGPT and Jasper now help SEO professionals create content that’s optimized from the start. From suggesting relevant keywords to improving structure and tone, these platforms accelerate content production without sacrificing quality.
AI can also optimize. Meta tags, headings, and even link suggestions can be fine-tuned using AI tools that learn what performs well in search engine results pages. For content marketers, it’s like having a digital strategist built into your workflow.
Predictive SEO and Smarter Keyword Research
AI has also taken the guesswork out of keyword research. Platforms like Ahrefs and SEMrush use machine learning to identify rising trends, track keyword difficulty, and forecast which terms are worth targeting. This predictive power gives SEO teams a major edge—they can align content with what users are about to search for, not just what they searched last month.
This kind of foresight wasn’t possible in earlier phases of SEO history. It’s made the industry more data-driven and forward-thinking than ever.
Automation of Repetitive SEO Tasks
If you’ve ever spent hours optimizing title tags or building outbound links, AI now has your back. From automating technical audits to suggesting internal links and tracking mobile search performance, AI handles the boring parts so you can focus on strategy.
Even off page factors like link outreach or reputation monitoring can be partly automated. This shift has redefined productivity in the SEO industry—and it’s raised the bar for what “optimized” means.
Search Engines Fight AI Spam
But not all AI-generated content is good. As automated tools flooded the web, Google had to respond. The Helpful Content Update (2022) and its 2024 Core & Spam Updates targeted AI-written pages that were generic, repetitive, or clearly written for search engines—not people.
Today, Google’s algorithm can spot AI fluff from a mile away. It rewards authenticity, inbound link relevancy, and useful, human-first content. If you’re leaning on AI to create content, it better sound like it came from someone who actually knows their stuff.
Search Results Are Now Conversational
Perhaps the most dramatic change is what search results look like. In 2025, search engine results aren’t just a list of links—they’re smart answers. Google introduced AI Overviews and Gemini-powered AI Mode, offering synthesized responses right at the top of the page.
That means the traditional click-through model is disappearing. To stay visible, your content has to be good enough to be quoted by the AI—or at least compelling enough to drive clicks from users who are now used to getting instant answers.
When Did Google Become Important in SEO History?
Google became important in SEO history in 1998, when it launched with the PageRank algorithm—a breakthrough that transformed how search engines ranked web pages.
Developed by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, it treated every external link like a vote of confidence. The more high-quality links a page had, the more trustworthy it seemed.
This idea flipped search engine optimization upside down. Suddenly, it wasn’t enough to stuff a page full of keywords or manipulate meta tags. You needed backlinks—real, relevant ones. And just like that, Google redefined what it meant to earn a top spot in search engine results.
By 2000, Google doubled down on its link-based model by launching the Google Toolbar. For the first time, SEO professionals could see PageRank scores for any site, right in their browser. That tiny green bar sent a message: links mattered. A lot. Almost overnight, link building became the heartbeat of SEO strategy.
As Google’s search engine results became more relevant, faster, and less spammy than those of other search engines, it didn’t just rise in popularity—it became the default. By the early 2000s, optimizing for Google was SEO. And from that point forward, the entire SEO industry followed Google’s lead—one algorithm update at a time.
What Was the First Search Engine Optimization Company?
It is believed, that the very first company widely recognized for offering SEO as a professional service was Webstep Marketing, which started using the term “search engine optimization” in 1997. At a time when few outside tech circles even knew what search rankings were, Webstep positioned SEO as a strategic service—helping turn it from a practice into an industry.
Their use of the term helped legitimize SEO in the business world. As Google’s PageRank shifted focus toward inbound link relevancy and high-quality web pages, other SEO companies followed. Soon after, industry pioneers like Bruce Clay and Danny Sullivan (via Search Engine Watch) helped define the foundations of the modern SEO strategy.
What Were the First SEO Tools?
One of the first true SEO tools was WebPosition Gold, launched in 1997 to help webmasters track search engine rankings, research keywords, and submit websites to multiple search engines.
In the mid-to-late ’90s, search engine optimization was still a new concept, and SEO tools were built to solve practical problems. Getting listed in search results wasn’t automatic—you had to submit your site manually. Tools like SubmitWolf (1997) made that process easier, offering bulk submissions to thousands of early search engines and directories.
AddWeb, introduced in 1998, expanded on that by combining site submissions with keyword tracking and link popularity analysis. It was one of the first signs that SEO software could do more than just submissions—it could shape strategy.
By the 2000s, more advanced platforms emerged. SEOmoz (now Moz) launched in 20024, followed by Google Webmaster Tools in 2025. These gave users direct feedback on how their sites performed in search engine results. Later came SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Ubersuggest, offering deep insights into backlink profiles, keyword opportunities, and search engine performance.
Start free trial and bring modern SEO tactics to every page you launch.
Understand SEO History to Boost Landing Page Traffic
Landing pages live or die by visibility. You can have the perfect offer, copy, and design—but if no one finds the page, it won’t convert. That’s where understanding the history of SEO becomes a real competitive advantage.
Since the moment SEO started in the 1990s, one thing has stayed constant: search engines reward content that meets their standards of relevance, clarity, and quality. Those standards have evolved—drastically. The early days of keyword stuffing gave way to PageRank and link building. Then came mobile-first indexing, natural language processing, and AI-powered search results. Every chapter in the evolution of SEO has changed what it takes to rank.
That’s where Landingi comes in. The platform gives you full control over how your landing pages are built, structured, and optimized. Whether you’re refining content for search intent or ensuring mobile-friendly speed, Landingi helps you apply decades of SEO lessons without writing a single line of code. If you want your landing pages to show up, stand out, and convert—Landingi is where you start.