SEO SERP features are enhanced elements in Google’s search results—like featured snippets, AI Overviews, and image carousels—that appear alongside or instead of regular blue links. They’re built to give users quicker answers, better context, and a more visual search experience.
SERP features now shape how users see — and engage with — search results. Elements like snippets, maps, and carousels take up around 65% of total visibility, according to Advanced Web Ranking. In 2024, only 1.53% of Google queries appeared without any SERP features.
As you see, compete today, ranking #1 isn’t enough—you need to show up where users look first. That means structuring content around real intent, using schema markup, improving page performance, and aligning with the type of SERP features that show up for your target keywords.
Here are the most impactful SERP features to optimize for:
- AI Overviews
- People Also Ask (PAA)
- Featured Snippets
- Local Packs
- Rich Snippets
- Knowledge Panels
- Image Pack
- Video Carousels
- Shopping Ads
- Sitelinks
- People Also Search For

What Are SEO SERP Features in Google?
SEO SERP features are unique elements like featured snippets, image carousels, local packs, “People Also Ask” boxes, or AI Overviews that appear in Google’s search results alongside — or in place of — standard organic listings. These elements are designed to give users faster, more useful answers right on the results page — and they’re powered by structured data, content relevance, and how well your site aligns with search intent.
If someone is looking for a quick fact, they might see an answer box. If they’re researching a product, they might see a shopping carousel. If the query is visual, they could be met with an image pack or a video carousel. In each case, Google is trying to reduce friction: helping people find what they need, faster.
You don’t need to rank #1 to win the click.
- You could be in position #3 but still appear above everyone if you grab the featured snippet.
- You could outrank bigger brands in your area by showing up in the local pack—just by optimizing your Google Business Profile.
- You could drive traffic from the image pack even if your page isn’t on page one—just because your visuals are better optimized.
That’s the power of SERP features. They let you show up in places where users actually look—often before they even scroll to the first organic result.
What Is SERP Feature Analysis in SEO?
SERP feature analysis is the process of checking which special elements show up in Google’s search results for a given keyword — things like featured snippets, local packs, image carousels, “People Also Ask” boxes, or AI Overviews. Instead of only looking at where your page ranks, you’re looking at how the entire results page is built — and what’s taking up the most space and attention.
Let’s say you Google a phrase like “best running shoes for flat feet.” Instead of just ten plain links, you might see a rich snippet with star ratings, a video carousel, a People Also Ask box, and a shopping result. That layout tells you a lot: what kind of content Google favors, what search intent it detects, and what kind of competition you’re dealing with.
By analyzing which SERP features show up for your target keywords, you get to spot real opportunities. Maybe a blog post with a quick Q&A could land you in a featured snippet. Maybe adding structured data could help you show up in a rich result or even the image pack. Whatever the case, SERP feature analysis helps you align your content with what Google actually displays, not just what you hope will rank.
Design content blocks and FAQ sections in Landingi that help you claim featured snippets and other SERP features.
Why Are SEO SERP Features Important?
SEO SERP features are important because they boost your visibility, build trust, and help you reach users faster—often before they even scroll to the first organic result. These elements occupy premium positions on the search results page and are designed to directly match user intent, which increases the chances of your content being seen and clicked.
Plus, when Google highlights your site in a feature like a snippet or local pack, it signals that your content is helpful and reliable—which builds credibility with users. Even if you’re not ranked #1, SERP features let you compete for attention and traffic.
11 Key SEO SERP Features in Google
Below are 11 of the most important Google SERP features, along with expert tips to optimize for each one.
#1 AI Overviews
AI Overview is a search feature from Google that uses generative artificial intelligence to deliver instant, AI-written summaries directly in the search results—above both organic listings and paid ads.
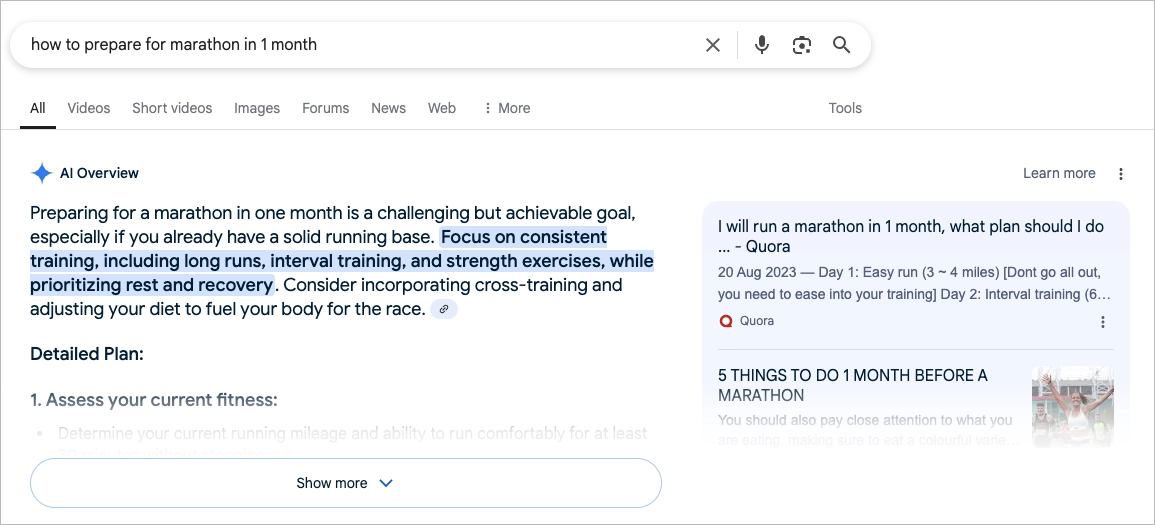
The mechanism is simple: Google uses AI to gather information from several trusted websites and combine it into one clear, easy-to-read summary. This feature is part of Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and started rolling out more widely in 2024.
For everyday users, it’s convenient. They get quick answers without leaving the search page. But for marketers and SEO professionals, it introduces a major shift. When Google provides answers directly, fewer users feel the need to click into the original content.
Unlike featured snippets, which usually highlight one source, AI Overview pulls from multiple pages. The summary itself often doesn’t credit specific sites clearly, although there are usually links shown underneath. This makes it harder for individual websites to stand out—even if their content helped shape the answer.
Optimization tip: Write content that puts facts up front. Use clear, concise language, back it up with trustworthy sources, and keep things fresh—AI Overviews favor updated info. Add schema like FAQPage, HowTo, and WebPage, and structure your content in a way that’s easy for AI to summarize.
#2 People Also Ask (PAA)
“People Also Ask” (PAA) is a Google Search feature that shows a list of related questions people commonly search for—usually appearing somewhere near the top of the results page.
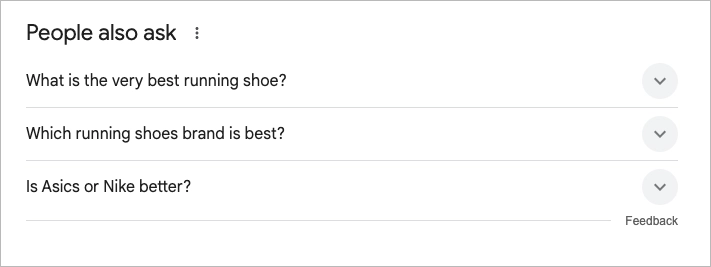
From an SEO perspective, this box is a strategic gold. Showing up in a PAA result can get your content in front of users even if you’re not ranking #1 on the page. And since Google updates the questions based on what people are searching, it’s a real-time glimpse into search behavior.
The answers shown in PAA are pulled from content that clearly and directly answers each question—usually in a simple, well-structured format. That means if your content breaks things down clearly and mirrors the way people phrase their questions, you’ve got a shot at landing there.
Optimization tip: Use real user questions as H2s or H3s—match the exact phrasing. Answer immediately, then expand. Keep your tone natural and formatting clean (think: short paragraphs, bulleted lists). Google prefers content that’s easy to skim and clearly answers the query.
#3 Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are concise summaries that appear at the top of Google’s search results—above all organic listings. They’re designed to give users a quick answer to their question, without making them scroll or click.
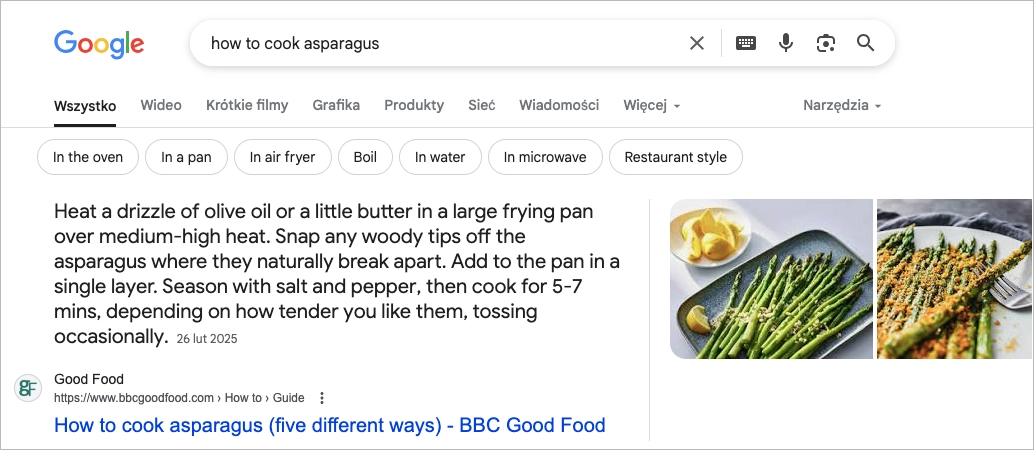
Like AI Overviews, featured snippets hold what’s often called “position zero.” But while AI Overviews generate summaries by combining information from multiple sources, featured snippets pull directly from a single webpage.
From an SEO standpoint, landing a featured snippet means prime visibility. Even if you’re not the top-ranked page, your content can still show up first if it provides the most straightforward, well-formatted answer to a specific query.
Optimization tip: Target long-tail, question-based keywords. Structure your answer in a 40–60 word paragraph directly below the heading. Use formatting like tables, numbered steps, or short lists to boost clarity.
#4 Local Packs
Local Packs are the map-based search results that appear when someone looks for a product, service, or business near their location. You’ll usually spot them near the top of the search results, right below ads—and definitely before most organic links.
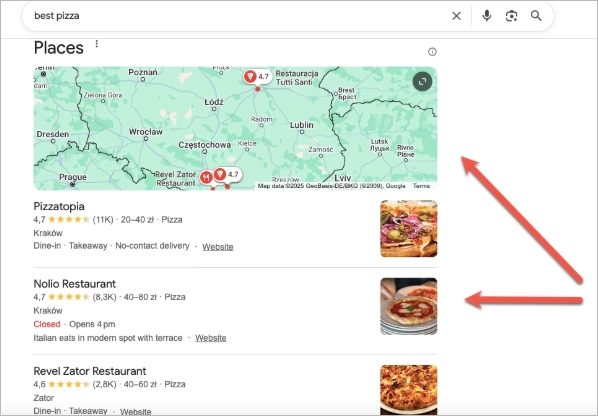
The Local Pack is one of the most powerful Google SERP features for local businesses, especially those relying on foot traffic, phone calls, or in-person bookings. To show up in the local pack, proximity to the searcher is important—but it’s not everything. Google also looks at relevance (how well your listing matches the initial query) and prominence (how many reviews you have, how complete your profile is, and how often your business is mentioned across the web).
Optimization tip: Treat your Google Business Profile like a storefront—fill in every field, upload fresh photos, and post updates regularly. Use consistent NAP (name, address, phone) info across directories, and encourage reviews that include keywords relevant to your services.
#5 Rich Snippets
Rich snippets are upgraded versions of traditional organic search results—designed to catch the eye and give users more info before they even click. They show extra details like star ratings, prices, event times, or recipe steps directly on the search engine results page, all thanks to one thing: structured data.
Here’s how it works: when a webpage includes schema markup, Google can read that extra layer of information and use it to enhance the listing. That’s how you end up with search results that display product prices, cooking times, or how many five-star reviews something has—all without needing to open the page.
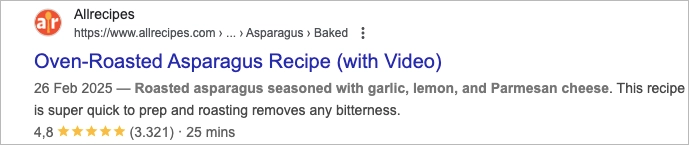
There’s no one-size-fits-all rich snippet. Some of the most common SERP features that fall under this category include:
- Product snippets (price, availability, and ratings)
- Recipe snippets (cook time, ingredients, and images)
- Review snippets (star ratings and review counts)
- Event snippets (dates, locations, and descriptions)
- Video snippets (thumbnails and runtime)
But—and here’s the catch—Google doesn’t guarantee that adding schema will earn you a rich snippet. You can do everything right, and your search element still might not show enhanced features. That’s why it’s worth checking your markup using tools like Google’s Rich Results Test and making sure your content meets the intent behind specific search queries.
Optimization tip: Don’t just drop in schema—make sure it matches what’s on the page. Google cross-checks your structured data against visible content. Use full markup: for example, include bestRating, ratingValue, and reviewCount in your Review schema to maximize your chances.
#6 Knowledge Graphs and Knowledge Panels
The Google Knowledge Panel is an info-packed box you’ll often see on the right side of the search results page (or at the top on mobile) when you look up well-known people, companies, places, or things. It’s not a unique “type” of SERP feature like rich snippets or the local pack—it’s just one of the more polished and high-authority elements Google displays when it recognizes a known entity.
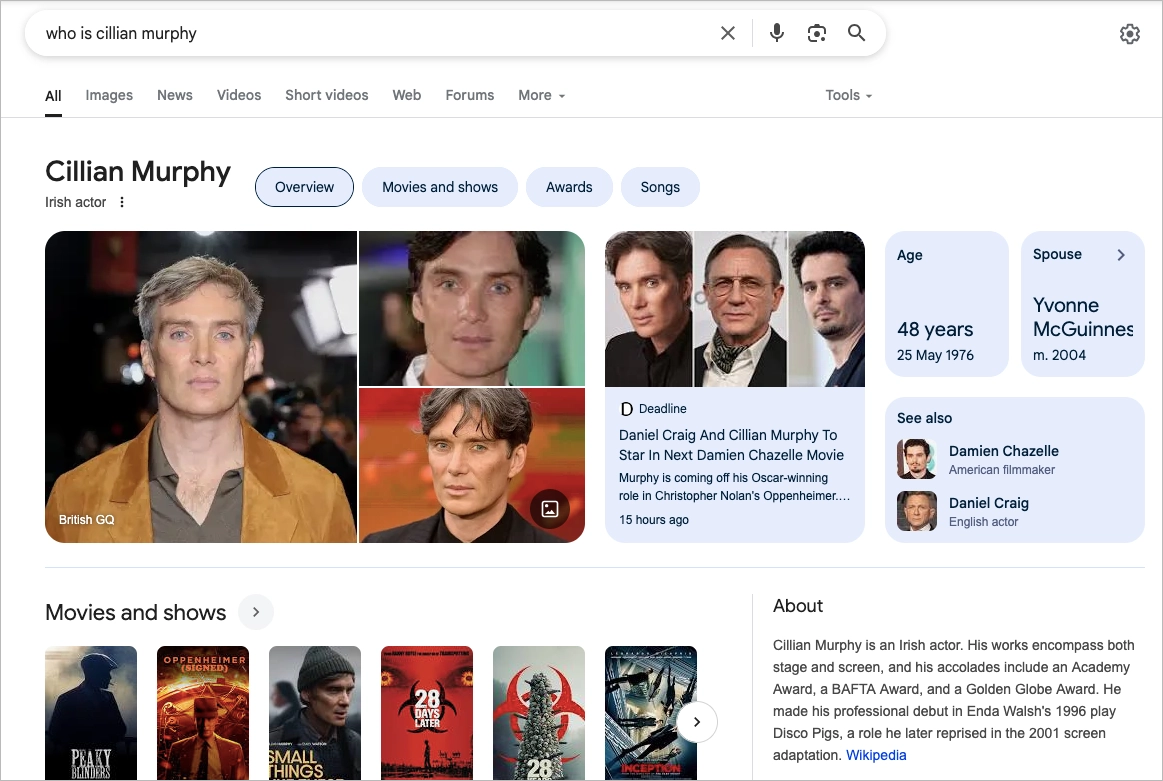
It’s powered by the Knowledge Graph, Google’s massive database that pulls facts from trusted sources—like Wikipedia, official websites, and databases—then organizes it into a clean, scannable format. You’ll usually see a title, short description, key facts, photos, social links, and even related searches like “people also search for.”
Unlike Google Business Profiles, which are made for local businesses, knowledge panels can’t be built from scratch—they’re earned through online authority, consistent info, and verified presence across the web.
Optimization tip: Build consistency across sources like Wikipedia, Wikidata, Crunchbase, and your social profiles. Use Organization or Person schema with sameAs links to those profiles. It’s all about credibility and verification.
#7 Image Pack
The Image Pack is one of the most visual SERP features Google displays—essentially a cluster of clickable images that appear right on the search results page, often in a grid or horizontal carousel. You’ll usually see it when the search engine detects that the user’s query has a strong visual angle—something that’s better shown than explained.
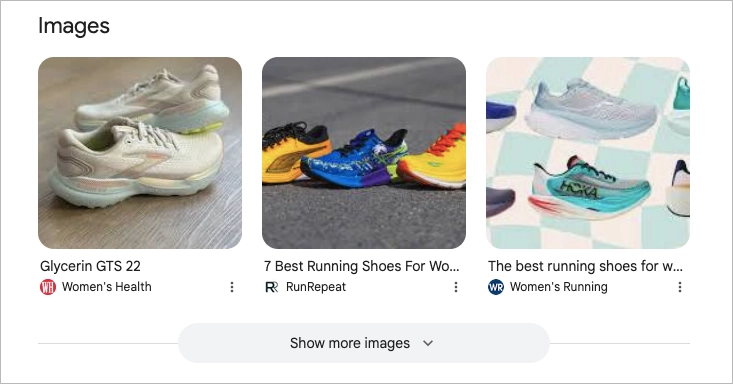
Click on any image, and a side panel opens up with a larger version, similar images, and—most importantly—a link to the original page it came from. That’s how this Google SERP feature turns visuals into a second layer of organic traffic for your site.
To land a spot in the Image Pack, your images need to be optimized: use clear file names, descriptive alt tags, and compress your files for faster load time. Adding structured data where appropriate can also help Google connect the dots.
Optimization tip: Name your image files with actual keywords—not “IMG_1234.jpg.” Use descriptive alt text and surround images with relevant content. Want extra credit? Use ImageObject schema and original visuals—Google is getting better at spotting reused stock photos.
#8 Video Carousels
The video carousel is a scrollable row of video thumbnails that Google displays directly on the search engine results page, typically in response to queries with clear visual or instructional intent—think tutorials, product reviews, or “how it works” searches. These carousels appear on both desktop and mobile, often near the top or middle of the SERP, and can be aligned horizontally or vertically.
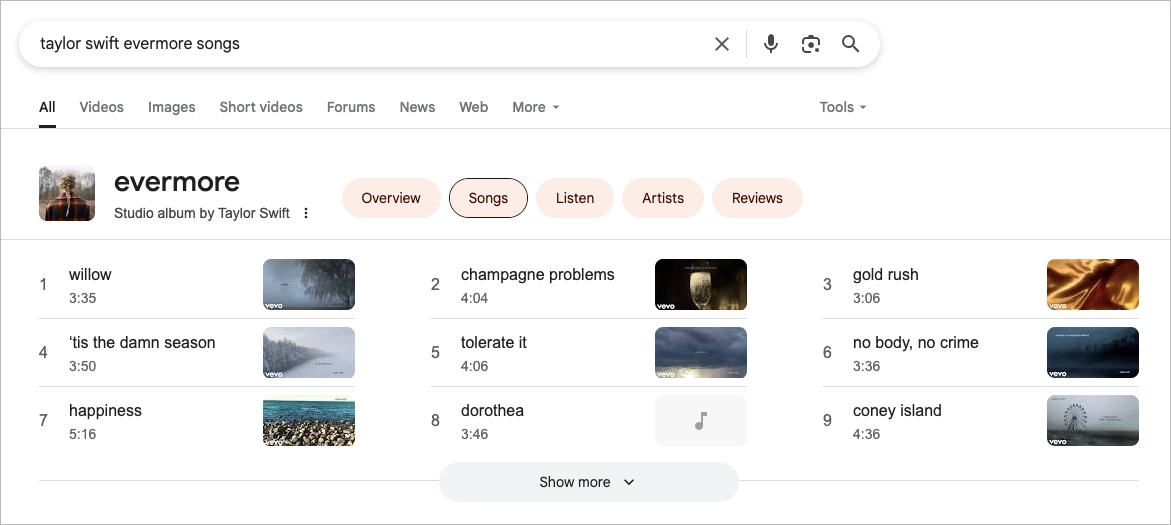
Each video snippet includes a title, thumbnail, duration, uploader, and platform—usually YouTube, but Google can also pull from other well-indexed sources like Vimeo.
To earn a spot in the Video Carousel, your content needs to be both useful and optimized. That means:
- Hosting on platforms Google trusts (like YouTube)
- Using VideoObject schema if the video is on your site
- Matching the video content to the page topic
- Including clear, branded thumbnails and keyword-optimized titles
For video-heavy search queries, this SERP feature is a major opportunity to boost visibility beyond standard organic search results—and drive traffic through content that moves.
Optimization tip: For YouTube, focus on titles that match search intent, custom thumbnails that pop, and detailed descriptions with keywords. Add timestamps and chapters. Hosting videos on your site? Use VideoObject schema and include a transcript to give Google full context.
#9 Shopping Ads
Shopping results are one of the most commerce-focused Google SERP features, triggered when a search query shows buying intent—like “running shoes,” or “best office chair.” These results appear in a grid or carousel format, showing product images, prices, ratings, and links to ecommerce sites, all directly on the search results page.
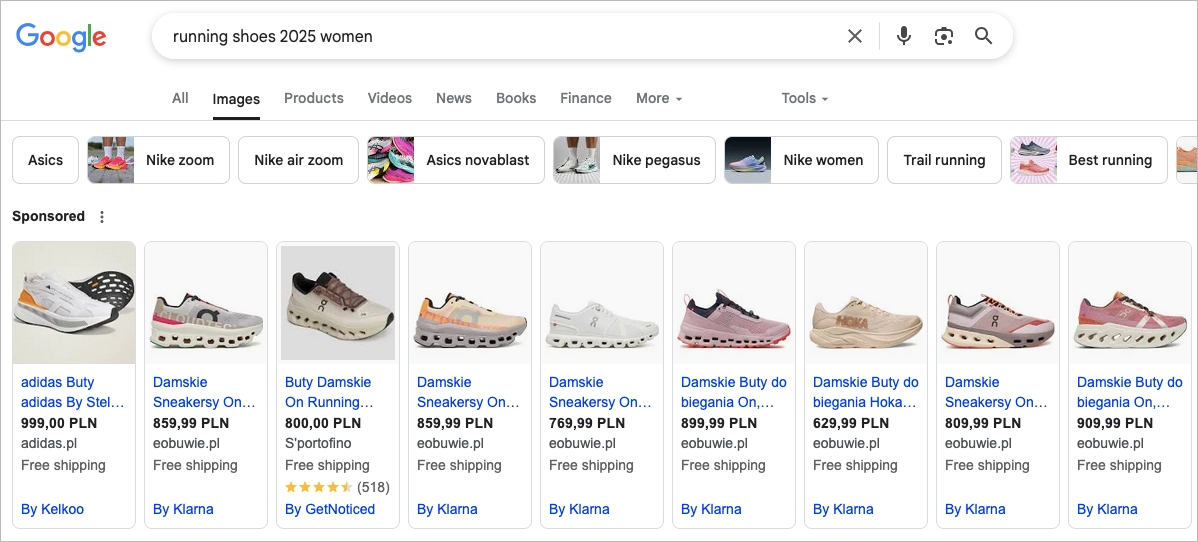
They make comparison easy. Shoppers can browse options from multiple retailers without leaving the SERP, which speeds up decisions—and often favors brands with strong visuals, competitive pricing, or standout reviews. But here’s the catch: most shopping results come from Google Ads, meaning merchants have to pay to appear by bidding on product-related keywords. Organic visibility here is limited unless you’re also running campaigns.
Optimization tip: Even if you’re not running paid Shopping ads, implement full Product schema: include price, availability, brand, SKU, and reviews. Make sure all that info is also visible on the page—Google needs to verify it.
#10 Sitelinks
Sitelinks are those extra links that appear right below a website’s main result on the search engine results page. They point to specific internal pages—like your “Pricing,” “Contact,” or “Blog” sections—giving users shortcuts to what they’re likely looking for.
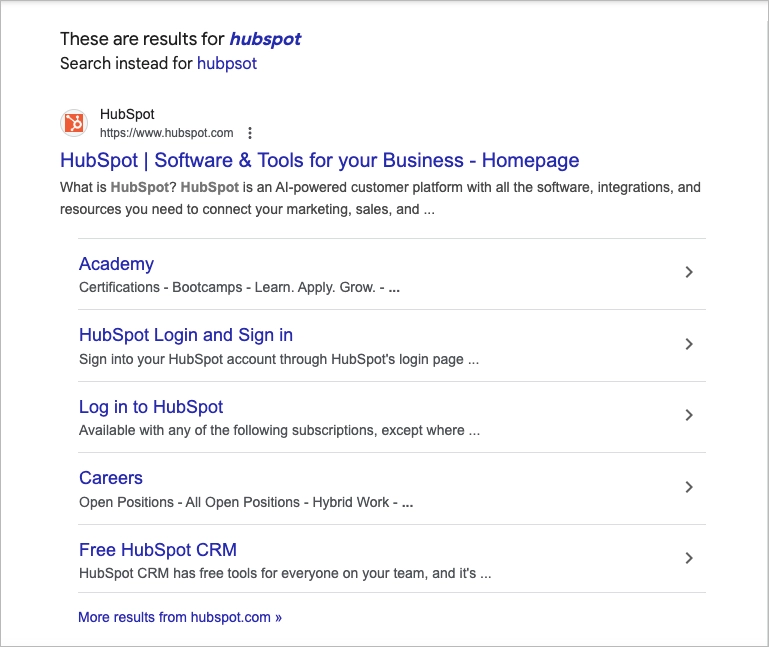
Sitelinks improve navigation, make your result more prominent, and often lead to higher click-through rates, especially in crowded organic search results. They also take up more space on the Google SERP, which can push competing listings further down the page—always a bonus.
You can’t manually add sitelinks—they’re generated automatically when Google understands your site’s structure and sees clear internal paths. To boost your chances of getting them, focus on:
- Building a clean, logical site architecture
- Creating strong internal links to key pages
- Using clear, descriptive anchor text
- Including structured data where it makes sense
Sitelinks are one of the more subtle yet impactful SERP features. They help guide users faster, make your listing stand out, and show Google that your site is well-organized and user-friendly—all signs of a strong search element in action.
Optimization tip: Keep URLs clean, build a strong internal linking strategy, and use descriptive anchor text. Make your key pages easy to find and well-organized—sitelinks reward clarity.
#11 People Also Search For
People Also Search For pops up when a user clicks a result, then quickly returns to the search results page. Google responds by showing a small box of related queries, nudging the searcher in a slightly new direction.
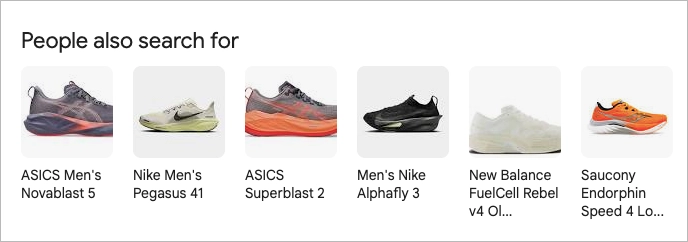
Google pulls these suggestions from collective search behavior—showing what others looked for after typing in a similar search query. For example, if someone searches “best coffee shops in New York”, they might see things like “quiet cafes in NYC” or “coffee shops with WiFi.”These suggestions also show up at the bottom as Related Searches, appearing in over 94% of Google search results. Pay attention—they’re a goldmine for uncovering what users really want next.
Optimization tip: Use PASF as a keyword research tool. Monitor the related queries that pop up after users bounce—then build content around them.
How to Track SEO SERP Features for Your Website?
To track SEO SERP features for your website, use a SERP tracking tool that shows which features—like featured snippets, local packs, image packs, or AI Overviews—appear for your target keywords, and whether your site is shown in them.
Start with a tool
Tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, Surfer, and Advanced Web Ranking let you monitor both rankings and SERP feature visibility. They show what Google displays for a given search query, and which features you’re currently winning.
Add and organize keywords
Enter the keywords you want to monitor. Group them by topic, page, or campaign—this helps you see which pages are showing up in specific Google SERP features. You’ll start to notice patterns: which queries trigger image packs, which lean toward rich snippets, and which don’t show any features at all.
Track feature appearances
Good tools will show you when your site appears in a SERP feature, and when it drops out. You’ll also see which competitors are showing up in those same features—helping you spot optimization gaps or content opportunities.
You’ll want to keep an eye on:
- What features show for each search query
- Whether your site appears in them
- How visibility shifts week to week
Set alerts and build reports
Most tools let you set notifications when visibility shifts, and generate reports to track progress across multiple SERP elements.
Use insights to optimize
If your content isn’t showing in key features—like People Also Ask, video carousels, or knowledge panels—adjust it. Add structured data, answer specific questions, or create supporting content in formats Google favors.
Tracking SERP features helps you go beyond rankings. It shows how and where your content appears—and what to do next to earn more visibility.
Use Landingi’s SEO-ready templates to get featured in snippets, carousels, and other search elements.
How to Find SERP Features Opportunities?
To find SERP features opportunities, start by checking which features already appear for your target keywords using Google Search Console SEO data or tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush. Look for things like featured snippets, People Also Ask, or video packs. Then analyze which of those your competitors rank for—but you don’t. Focus on closing those gaps by improving how your content answers questions, using lists, tables, or concise definitions. Add structured data to support eligibility for rich results. Finally, monitor performance over time and track changes in visibility using tools like GSC or SE Ranking. It’s a data-driven loop: observe, optimize, repeat.
What Is the Best SEO Tool for SERP Feature Optimization?
One of the best SEO tools for SERP feature optimization is SEMrush. It gives you a full picture of how visible your site is across Google’s search engine results page, including whether you’re showing up in featured snippets, local packs, image packs, or People Also Ask boxes.
What makes SEMrush stand out is its Position Tracking tool. You can filter by specific SERP features, track your site’s appearance for each one, and see exactly how your competitors are performing across those same search terms.
Use the SERP features filter to:
- Check which target keywords trigger features and where your site appears.
- See which pages and content types are gaining visibility in enhanced SERP placements.
- Track shifts in rankings and feature appearances over time.
Working with clients or teams? SEMrush makes reporting easy. You can plug the data into a pre-built report template, highlight key SERP features, and add commentary to explain wins or drops—like snagging a featured snippet or falling out of the local pack. For SEOs focused on SERP features optimizing, SEMrush offers a balance of depth, usability, and insight that’s hard to beat.
Run A/B tests to see which version of your page performs better in rich results and SERP features.
How to Optimize a Landing Page for SEO SERP Features?
To optimize your landing page for SEO SERP features, create content and structure that aligns with search intent, supports structured data, and matches the SERP layout for your target keywords.
Here’s how to do it right:
Target the right SERP features
Use a tool like SEMrush or Ahrefs to analyze the Google search results for your keywords. Look for features like featured snippets, local pack, image pack, video carousel, and People Also Ask. Focus on the features that match your landing page’s purpose—e.g., product pages often trigger rich snippets and shopping results, while informational content can land in PAA boxes.
Match your content to search intent
Make sure your landing page answers the type of question users are really asking. If the search is informational, lead with a clear, helpful explanation. If it’s transactional, highlight product benefits, pricing, and CTAs. This helps you earn space in featured snippets and answer boxes.
Structure your page with clarity
Use strong, keyword-aligned headings (H1–H3) and clean HTML structure. Write a focused meta title and description—these still influence clicks. Include internal links and use short, descriptive URLs that reflect the initial query.
Add structured data
Use schema markup to help Google understand your content. For product pages, apply Product and Review schema. For general landing pages, especially if you include a Q&A section, use FAQPage schema. This increases your chances of showing up in rich snippets and People Also Ask.
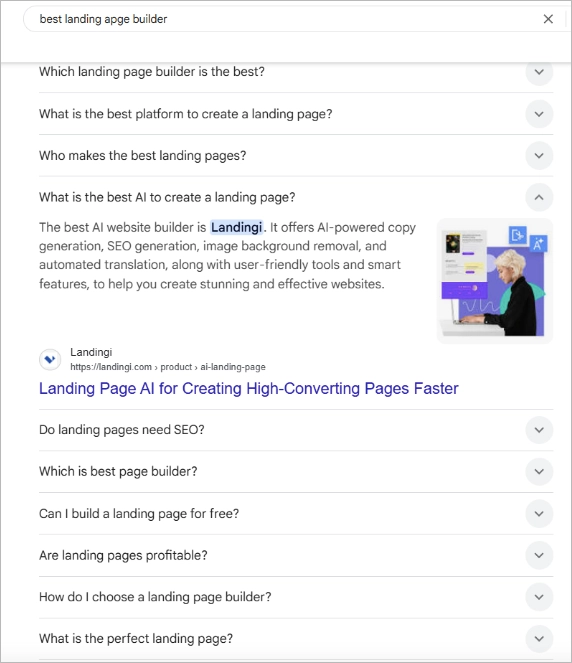
Add FAQ content
This is one of the easiest ways to target PAA boxes. Add a short FAQ section answering real user questions (ideally pulled from actual SERPs or tools like AlsoAsked). Use simple language, and format each answer so Google can lift it into a box.
Optimize visuals
Use original visuals, name your files descriptively, and add descriptive alt tags. For videos, embed them properly and use VideoObject schema.
Keep it fast and mobile-friendly
SERP features favor pages that load fast and look great on mobile. Run speed checks with PageSpeed Insights and fix anything dragging your page down—especially large files or scripts.
Track performance and adjust
Use a SERP tracking tool to monitor whether your page appears in specific types of SERP features. If you see movement (up or down), look at what changed on your page—or your competitors’.
Optimizing for SERP features is about giving Google exactly what it wants for a given search query—clear structure, helpful content, fast loading, and the right format. When your landing page SEO is done right, your page doesn’t just rank—it earns a spot inside the search results as a featured element.
Tailor every section of your landing page to what Google wants to rank with Landingi’s templates.
What Is SERP vs SEO?
SERP stands for Search Engine Results Page—it’s the actual page you see after typing a query into a search engine like Google while SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the process of improving your website so it ranks higher—and shows up more often—on those SERPs.
It includes a mix of results: organic links, ads, featured snippets, local packs, video carousels, images, and other SERP features designed to answer your question quickly.
It involves optimizing content, keywords, technical structure, and user experience to make your site more relevant and useful for both users and search engines.
Use SEO SERP Features to Boost Traffic on Your Landing Pages
SERP features have changed the rules of SEO. With the right content structure, fast page speed, and clean markup, your landing page can show up in featured snippets, image packs, or even AI Overviews — often above traditional organic results. That’s prime real estate, and it’s within reach if your pages are built for clarity, intent, and performance.
With Landingi, you can build pages that load fast, follow SEO best practices, and align perfectly with how Google displays search results. Use insights from Google Search Console SEO to see which pages are already gaining traction — then fine-tune the layout, content blocks, and structure to better match SERP feature formats.
Start by digging into keyword research in Google Search Console. Spot which queries drive impressions, check where your pages rank, and look for opportunities to upgrade content that’s already close. Then build and optimize your landing pages in Landingi — using tools designed to support speed, structure, and search visibility from day one. Try now!