For many businesses, conversion is the ultimate goal.
They’ve heard of it and want it, but they’re often unsure how to achieve it or recognize it when it happens. Is it a purchase? A form submission? A new lead? It can be any of these. A conversion is a meaningful action a user takes that contributes to your business objectives. This might include booking a demo, downloading a guide, or signing up for emails.
Conversions occur after the click, not within ads or social media posts. That’s the role of landing pages. They guide visitors toward taking a single, focused action. When a landing page is not optimized for conversion, effective messaging and targeting won’t be enough.
This guide explains what conversion means in marketing, outlines its types, and provides specific real-world examples. You’ll learn what to aim for and how to achieve it.

What is Conversion in Marketing?
Conversion in marketing means a potential customer takes a specific action that supports a business goal. This could be making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or requesting a product demo.
According to Neil Patel, conversion is “turning a visitor into a customer.”
What is Conversion in Digital Marketing?
In digital marketing, a conversion is when a user completes a specific goal, such as downloading an eBook or subscribing to an email list. It represents the online version of traditional marketing outcomes.
Because digital actions are trackable, you can monitor performance in real time using analytics tools. This helps measure campaign success and adjust strategies based on actual user behavior, such as click-through rates or form completions.
What is Conversion in Advertising?
In advertising, a conversion happens when someone who sees an ad takes a desired action, such as clicking on a pay-per-click ad and making a purchase. It can also refer to actions taken after viewing the ad, like using a promo code during checkout.
For example, when an ad includes a discount code and a customer applies it while purchasing, that action counts as a conversion.

Using a discount code seen on TV? That counts as a conversion too.
What is Conversion Rate in Marketing?
Conversion rate is a metric that measures how effectively a marketing strategy turns visitors into customers. It’s calculated by dividing the number of conversions by the total number of visitors, then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
For example, if 100 people visit your website and 10 make a purchase, your conversion rate is 10%.
This metric is a key performance indicator (KPI) for businesses and agencies. A strong conversion rate shows that marketing efforts are working. It also helps agencies better understand their audience and improve future campaigns.
What is Conversion in B2B Marketing?
In B2B marketing, a conversion occurs when a potential client takes a specific action, such as filling out a contact form, downloading a whitepaper, or starting a free trial. These actions move the lead further down the sales funnel and help qualify them for follow-up. Tools like CRM systems can support this process by tracking and managing leads effectively.
What is Conversion in Business?
In a business context, conversion is the process of turning potential clients into paying customers. It reflects how effectively a company transforms interest into revenue and involves coordination across sales, marketing, and customer service.
What is Conversion in Sales?
In sales, conversion means turning a lead into a customer. This process often includes nurturing the relationship, addressing objections, and ultimately closing the deal.
What Does Conversion Mean in Product?
In product, a conversion happens when a user takes a meaningful action that signals engagement or intent—such as upgrading from a free to a paid plan, activating a core feature, or completing onboarding.
Improving product conversion often requires cross-functional effort. This might include rebuilding parts of your product team, integrating customer feedback into design decisions, or hiring skilled developers to refine user flows and reduce friction.
What are the Types of Conversion in Marketing?
Understanding the different types of conversions is essential for optimizing your marketing efforts. Each type reflects a specific stage in the customer journey and requires a tailored strategy.
Soft Conversion
A soft conversion is an action that signals user interest without immediate revenue impact. Common examples include signing up for a newsletter or following a brand on social media. These early-stage actions help build relationships and guide prospects toward deeper engagement.
Hard Conversion
A hard conversion directly generates revenue, such as making a purchase or subscribing to a paid plan. These actions represent the primary goals of most marketing campaigns.
Micro Conversion
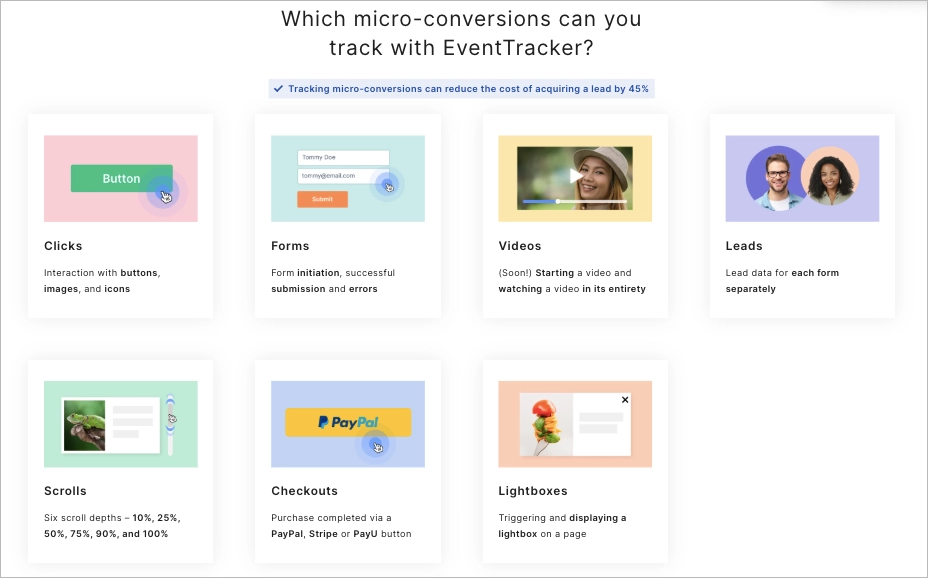
Micro conversions are smaller steps that lead toward a hard conversion. Examples include adding an item to the cart, clicking on a product description, or starting a sign-up process. These actions show intent and help identify points of friction in the funnel.
Using tools like EventTracker by Landingi, marketers can track micro conversions—such as clicks, views, form submissions, and payment events—and visualize them in built-in dashboards. This provides actionable insight for campaign optimization.
Macro Conversion
Macro conversions are the final actions that mark the completion of a business objective, like completing a purchase or signing a contract. They typically occur after one or more micro conversions and reflect a successful end to the customer journey.
What is Conversion Strategy?
A conversion strategy is a structured plan aimed at increasing the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action—such as making a purchase, filling out a form, or signing up for a service. It typically includes tactics like optimizing landing pages, conducting A/B tests, and using retargeting to re-engage potential customers.
For businesses in specialized industries, such as contracting, using tailored website services can help improve conversions by aligning design and messaging with the target audience’s needs.
What are Conversion Examples?
Conversions can take many forms depending on a business’s goals. Recognizing these different types helps tailor marketing strategies more effectively.
Make a Purchase on the Company’s Website
When a visitor completes a purchase, it’s a hard conversion that directly impacts revenue. This is often the primary goal of digital marketing efforts like paid ads or email campaigns. It reflects how well your sales funnel is working and how compelling your offer is.
Share a Post on Social Media
When someone shares your content on platforms like Facebook or X (formerly Twitter), it counts as a soft conversion. While it doesn’t generate revenue directly, it expands your reach, increases brand visibility, and can lead to future conversions. It also shows that your content resonates with your audience.
Make a Phone Call to the Company
When someone calls your business after visiting your website or seeing an ad, it signals strong interest. If the call results in a sale, it’s considered a hard conversion; otherwise, it’s a soft conversion focused on inquiry or engagement. Phone calls are often driven by well-placed calls to action and can be a key step in the customer journey.
Tracking these calls helps identify which marketing channels are generating the most qualified leads.
Fill Out a Form or Complete a Survey
Form submissions and survey completions can count as soft or hard conversions, depending on how the data is used and what follows. These actions provide valuable customer insights and often act as early steps in the conversion funnel—leading to purchases, subscriptions, or consultations.
Monitoring the performance of these actions helps refine lead generation and targeting strategies.

Sign Up for a Newsletter
Newsletter sign-ups are a classic example of a soft conversion. This action shows interest in your brand and opens the door for long-term engagement through email marketing. It’s often used to nurture leads until they’re ready to make a purchase.
A high sign-up rate suggests strong audience engagement. For example, subscribing to a newsletter for CTOs provides value to the reader while giving marketers a point of contact for future outreach.

Download a Free eBook
Downloading a free eBook is another soft conversion. It delivers immediate value to the visitor and captures their contact details for future marketing. This type of action often serves as an entry point in the customer journey.
Tracking download activity helps identify which content topics and formats are most effective at engaging your audience.

Register for a Free Trial
Signing up for a free trial is a meaningful action that can qualify as a hard conversion if it leads to a paid subscription. It gives potential customers hands-on experience with the product, helping them evaluate its value before committing.
This type of conversion is especially common in SaaS and subscription-based models. A high trial-to-paid conversion rate signals strong product-market fit and effective messaging.
Attend a Webinar
Webinar attendance is typically a soft conversion that reflects strong interest in a specific topic. It gives your business a chance to demonstrate expertise, deliver value, and connect with a targeted audience.
Webinars also serve as a lead generation tool by capturing registrant data. High attendance rates often reflect effective promotion and relevant subject matter.
Leave a Product Review
Leaving a product review is considered a soft conversion. It suggests a customer not only used the product but is invested enough to share feedback. Reviews function as social proof and can influence future purchasing decisions.
Monitoring reviews helps gauge customer satisfaction and uncover areas for product improvement.

Clicking on a “Buy Now” Button on a Landing Page
Clicking on a “Buy Now” button on a landing page is a hard conversion, as it directly leads to a sale. This action is the result of effective landing page optimization, compelling product descriptions, and a seamless checkout process. It’s a critical metric for evaluating the success of specific marketing campaigns, such as PPC ads or promotional offers. A high click-through rate on this button is a strong indicator of a well-designed landing page.

Why Landing Pages Are the Best Place to Trigger Marketing Conversions?
Landing pages are highly effective for driving conversions because they remove distractions, focus the message, and guide users toward one specific action. Every element—headline, body copy, and call-to-action—is aligned with a single goal, such as collecting leads, generating sales, or prompting sign-ups.
They also allow you to align content with the visitor’s intent. Whether the user arrives via a PPC ad, email, or organic post, the landing page can reflect the exact offer or message that brought them there. This alignment builds trust, enhances relevance, and increases the likelihood of conversion.
Another advantage is measurability. Landing pages can be tested, tracked, and optimized using tools like A/B testing, dynamic content, and analytics. This lets marketers lower acquisition costs, improve performance, and scale what works. In short, landing pages give full control over the conversion journey—turning traffic into results.
Boost Your Conversions with High-Performance Landing Pages
If you want to increase conversions, choose a platform with reliable tools that support every stage of your digital marketing process.
With Landingi, you gain access to a full suite of conversion optimization features—such as A/B testing, event tracking, and detailed analytics—to help you make data-driven decisions. You can also save time using over 400 pre-designed, conversion-focused templates and AI-powered copy generation. Features like Smart Sections and Dynamic Content allow you to scale and personalize your campaigns more effectively.
Test the platform with a free trial and see how it fits your marketing goals before committing.






