Did you know that Google Tag Manager is used on nearly 5 billion websites? Learn what Google Manager does, what are the benefits of implementing Google Tag Manager and how to set up a Google Tag Manager account.
Google is a solid and uncompetitive player in the digital world. Its search engine receives over 77,000 searches per second (according to Internet Live Stats study), which adds up to more than 4 000 000 searches per minute. No wonder Google decided to expand its operations and kicked off with offering a wide range of other services, like for example Google Tag Manager.
Google Tag Manager is not the most popular tool used in marketing campaigns. The reason behind it is the fact that dozens of business owners and marketers do not truly realise that such a tool exists, and that it can assist in working miracles for businesses. It’s much easier to understand how to use landing page templates than some mysterious management system.
But did you know that at least 4,990,427 live websites use Google Tag Manager? It can turn out to be extremely helpful when it comes to improving websites, landing pages performance and overall efficiency of businesses.
Once you read this article you will know:
- what is Google Tag Manager,
- why you should use Google Tag Manager,
- how to install a Google Tag Manager on a website,
- what are the basic components of Google Tag Manager,
- what are the best use cases for Google Tag Manager.
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager (GTM) definition states it is a tag management system (TMS) allowing its users to add little fragments of custom or template codes (tags) to URLs (websites) in order to get more detailed insights about traffic on a chosen website without having to modify the code (Google Tag Manager code needs only to be embedded into a website).
Below you can find a simple example of how GTM works. Information from one database (website) is shared with another database (Google Analytics, Google AdWords or other tools) through Google Tag Manager.

Source: https://www.analyticsmania.com/post/reasons-why-you-should-use-google-tag-manager/
Tools like Google Analytics provide you with a general view of your website or landing page performance. However, once you use Google Tag Manager as well, you are able to track each and every subpage, resources downloaded from your website, and to dictate exactly what data should be sent to Google Analytics.
Why you should use Google Tag Manager

Source: https://karenbusolinblog.wordpress.com/tag/how-to-use-google-tag-manager/
Easy to implement without coding knowledge
The usage of the tool is highly intuitive, so you need neither experience nor coding knowledge to implement it. You can make changes whenever you want once you insert a container tab. It is also very quick to implement and takes less than an hour.
What is more, Google Tag Manager comes with debugging tools, built-in error checking, version controls and preview mode enabling to check and test everything before it goes live.
Advanced tracking
Using Google Tag Manager enables you to take your users and traffic analysis to the next level and significantly improve your marketing strategy. You get highly useful and valuable data, which is one of the most essential functions of Google Tag Manager for your business.
Apart from that, you are not limited exclusively to tracking websites. You can also track:
- performance of YouTube videos on your site,
- print resources download statistics,
- AJAX form submissions.
Google Tag Manager is free of charge
Last but definitely not least, GTM is free, so you don’t need to worry about getting funds to make use of this tool. You can gain access to all its robust features, including usability, accounts, supported tags or user roles without paying a penny.
How to install a Google Tag Manager on a website?
In order to launch your GTM account:
- Go to tagmanager.google.com.
- Create an account or use an already existing one.
- Create a name for your account and choose a container (website, iOS, Android or AMP).
- You will be asked to embed given codes inandsection of your website.
- Now it’s about time to add tags, triggers and configure variables to chosen websites in Google Tag Manager dashboard.
What are the basic components of Google Tag Manager?
The basic components of GTM are:
- tags,
- triggers,
- variables.
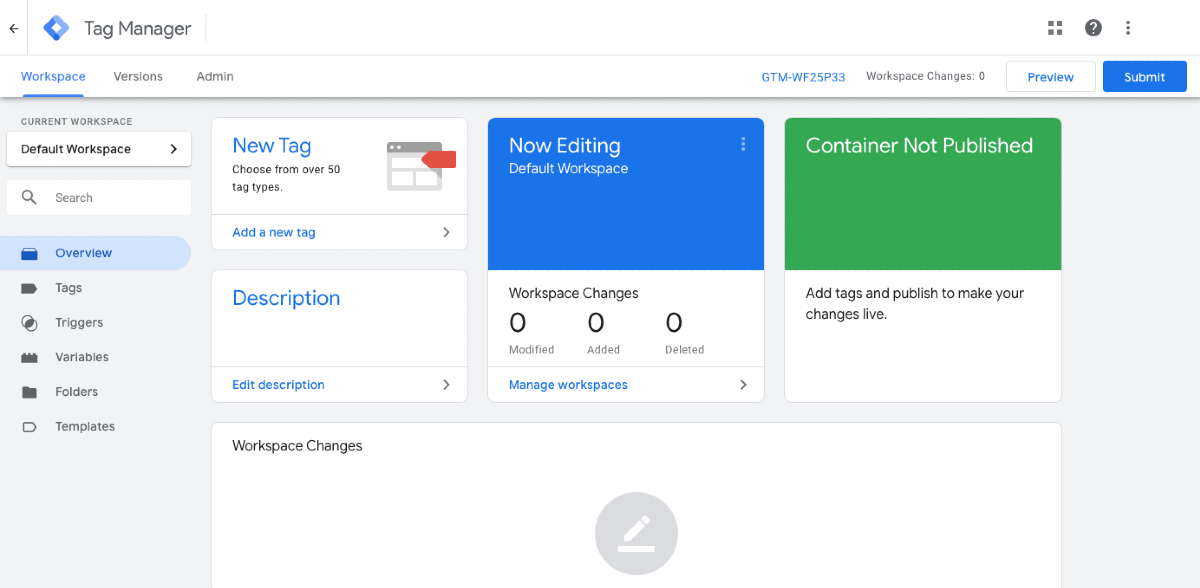
Google Tag Manager Dashboard
What are tags?
Tags are short codes enabling you to measure traffic on specific websites, monitor digital marketing campaigns and check users behaviour on particular sites. By using them, you can also implement codes, e.g. to display pop-ups when a specified action is performed. Tags also send data to reporting tools (like Google Analytics).
Consequently, they help in gathering all essential information to make appropriate and reasonable business decisions when it comes to creating your digital or content marketing strategy.
In order to set it up you need to click “add a new tag” and then:
- title it,
- choose its type (for example Classic Google Analytics or AdWords Remarketing – depending for what purposes you create a given tag),
- link the tag to Google Analytics,
- choose a trigger (find the definition below),
- save and submit.
What are triggers?
Tags fire in response to events and trigger are used to fire them when you want to. Therefore, triggers are associated to particular events such as:
- clicks,
- forms submissions,
- page views,
- page scrolls etc.
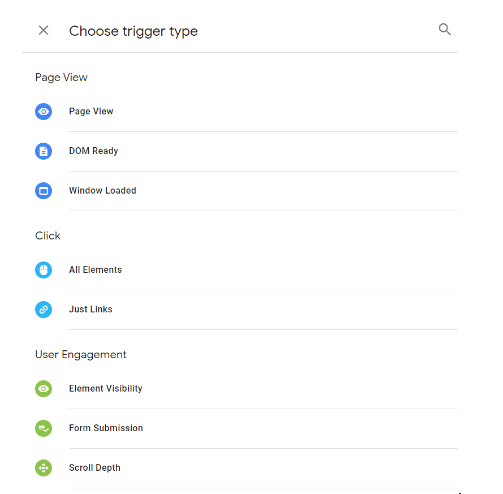
In GTM Dashboard you define the trigger and once an event that occurs matches the predefined trigger definition, tags that reference will fire.
What are variables?
According to Google definition, “A variable is a named placeholder for a value that will change, such as a product name, a price value, or a date”. In other words – variables is additional information GTM may use to take more data from a given website and provide this data to the tags or triggers when needed.
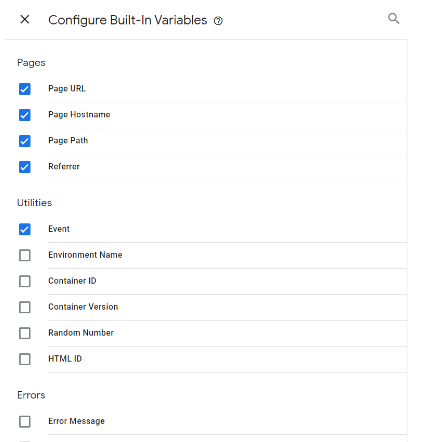
GTM has a lot of built-in variables but you can create custom ones. These common ones such as page URL, page hostname or event have been built in for you but you can add as many as you’d like.
All in all:
- tags are used to gather and report an interaction to a reporting tool (Google Analytics),
- triggers are used to observe and interaction and determine whether a given tag should be fired,
- variables are used to capture some data off the page and deliver this data to the tags and triggers once needed.
What are the best use cases for Google Tag Manager?
As mentioned – Google Tag Managers you to obtain more detailed insights about traffic and users of your homepage, landing page (created with the help of Landingi or using a landing page builder) and make better business decisions. However, the tool has a lot more to offer.
The best use case you are able to implement are:
- easy adjustment and publication of Google Analytics tracking scripts,
- conversions measurements by sending events to Google Analytics,
- setting up the Facebook pixel event using Google Tag Manager,
- conversion and remarketing pixels with Google Ads,
- running an A/B test with Google Optimize,
- GDPR compliance management.
Summing up, Google Tag Manager is a powerful tool that should be as widely used as Google Analytics already is. It provides you with a state-of-the-art analysis that can be extremely helpful when it comes to improving your marketing strategy, website or landing page performance, content marketing or video content strategy. It is completely free of charge and highly easy to implement, so you should not deprive your business of such a valuable weapon.