A popular SEO joke states that the best place to hide a dead body is on the second page of Google results. Sure, not ranking high enough is a common problem among websites owners. But you might also encounter an even more serious issue: what if your site doesn’t appear in search results at all?
Just imagine: you’ve worked for weeks or months on a new site, and you really like the result. It’s informative and well-designed, so you expect a good amount of traffic once you launch. And yet that traffic doesn’t materialize.
You try not to panic and run some searches that should lead to your site. Once again, it’s not there – not on the first page, not on the second, not even on the fifth.
What happened? Does Google hate you? Is your site somehow invisible? Have you done something wrong when coding?Onely reports that 16% of pages located on popular websites are not indexed by Google (T. Rudzki, Indexing in SEO – A Complete Guide for 2023). John Mueller from Google estimates that for 20% of sites worldwide, it’s absolutely normal not to be indexed (R. Montti, Google: It’s Normal for Pages of a Site to Not Be Indexed, 2021)!
In this post, I’ll tell you about the nine most important indexing issues, that may make your site not appear in Google search results – and how to fix them, making your site more SEO-friendly.
But before we jump to indexing problems and discover how to get your site indexed, let’s go first over some indexing basics.
Make your sections smartable and let go of mundane manual tasks with Smart Sections! An easy way to manage bulk changes.
Crawling vs indexing vs ranking: understanding the difference
In order to index a site, Google first needs to find it. The search giant uses special programs (called spiders) to crawl the web. A spider starts from a site it already knows. If it contains any links – external or internal – the bot crawls them, too. If they, in turn, contain links to other sites, the spider looks at those, and so on. This goes on 24/7, on billions of pages every day.
Whenever Google discovers a new page, it tries to understand what it’s about. It “reads” the title, headings, meta descriptions, content, pictures, videos, and so on. This information is added to the index – the complete list of web pages used by Google search.
Thus, when a user runs a search, Google doesn’t look for results on the web – it analyzes the index. It ranks all the relevant results in accordance with a complex (and secret) formula – and voila, your get your SERP (search engine results page). If you’d like to learn more about how Google Search works, watch this video.
Is Your site Really not Indexed by Search Engines?
It can happen that your page is indexed but doesn’t appear in the first few result pages. To see which is your problem, run a simple test:
type site:your-site’s-address in Google’s search bar.
Don’t forget to insert your website’s URL, obviously.
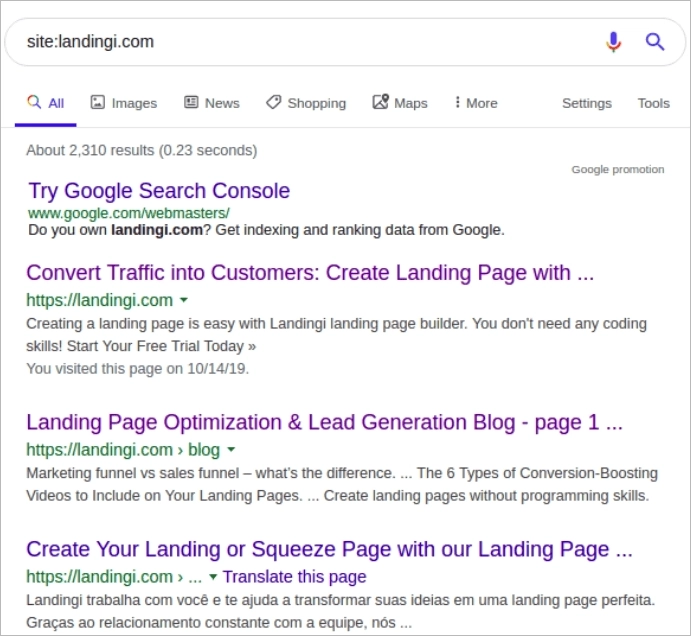
Note the number of indexed pages. If it looks right to you, then your site is properly indexed. Keep in mind that not all pages of a site must be indexed, however.
If your page is indexed by Google but you still get little or no traffic, the problem could indeed lie in your SEO.
But if you discover that some or all of your pages don’t appear in the search, something must be wrong with the indexing. Read on to find out the possible reason. Don’t worry: whatever went wrong, it’s probably easy to fix.
Reason 1: Your site is too new
How long should it take for Google to index a new site? For most sites, the waiting period ranges from 4 days to 1 month. Some people report getting indexed faster, but there is also anecdotal evidence of indexing taking months.
If your site is only a few days old, wait for a week or so, then run the test again. If you are still not indexed, try to ask Google to do it for you.
Solution: fetch & render
Google Search Console has a great URL Inspection tool:
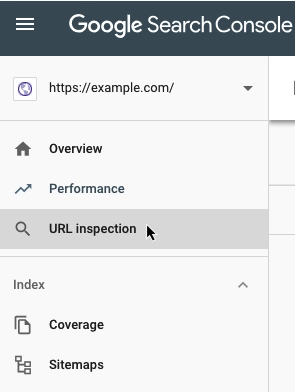
There, you enter the address of any page on your site or your whole domain, see their current index status, and request indexing. Google will send its bot to crawl and index your site, but it’s not an instant or guaranteed fix. It can easily take days, but since it’s so easy and free, why not try it?
Reason 2: You don’t have a sitemap
A sitemap is a document in the XML format that helps Google crawl and index pages. A sitemap contains detailed information about all the pages, when they were updated, what they contain, etc.

In theory, Google should be able to index your pages even without it. But if your pages aren’t well linked to each other – or if there aren’t many external links to your site – the normal crawling algorithm might not work so well. This is especially true for new sites. So I do recommend that you make a sitemap and supply it to Google.
Solution: sitemap generators!
How do they work? Let’s break it down into steps:
- Crawling the Website: Sitemap generators start by crawling the website’s structure and pages. This is similar to what search engine bots do when indexing a site. They follow links on the site to discover all accessible pages.
- Collecting Information: As the generator crawls the website, it collects essential information about each page, such as its URL, last modification date, and the frequency of changes. It may also gather additional metadata like page priority.
- Generating the XML File: Once the generator has collected all the necessary data, it compiles it into a structured XML file. This XML file adheres to the Sitemap Protocol, a standardized format recognized by search engines.
- Indexing and Submission: Website owners can take the generated XML sitemap and submit it to search engines like Google via their webmaster tools or search console. This step informs search engines about the sitemap’s location and its content.
- Regular Updates: Sitemap generators can also be configured to update sitemaps automatically at regular intervals or when significant changes are made to the website. This ensures that search engines always have access to the most current information about the site.
- Improving SEO: By providing search engines with a well-structured sitemap, website owners can improve the indexing and visibility of their content. It helps search engines discover pages that might be missed during the regular crawling process, leading to better SEO performance.
As you see, they do much more than only create a sitemap and get it indexed properly. They are also potent in improving a site’s visibility and driving more traffic.
Reason 3: “noindex” tag
The way your page is coded could be blocking Google from crawling it. It’s known as “noindex” tags, and they are often added while a page is still under construction. It makes sense: if your website is still not ready, you wouldn’t want anyone to stumble upon it, right?
You’ll know that your page is made invisible to crawlers if its section contains something like this:
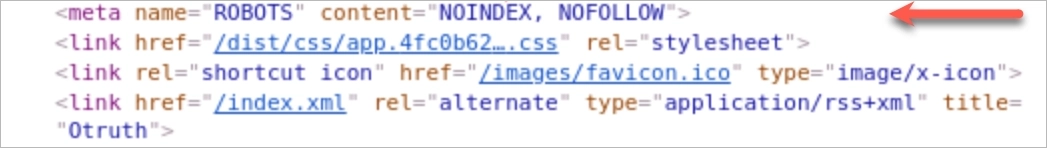
The first line in the above code instructs google crawl to omit your site. that Google won’t be able to crawl your site, but other search engines (such as Bing) will.
Solution: quick check
Check your pages’ sections and remove any “noindex” bits you find. You can read more about this issue here.
Reason 4: Canonicalization errors
The verbs “to canonicalize” or even “to canonical” can seem clumsy – and they are. But these are verbs that you need to know. A canonical version of a page is the one that Google treats as the main one or preferential if it encounters duplicate content. Perhaps you’re thinking, “but there’s no duplicate content on my site!”. Well, think again. Is there just one way to reach your homepage? For the site you are now reading, for example, there are several:
… and others. Any of these will work and look exactly the same – but for Google, they are four different pages with duplicate content! And if your site is translated into other languages, the problem is exacerbated – you’ll have even more “identical” pages.
A canonical tag is found in the section of a page and looks like this:

Solution: inspection
Run the Google URL Inspection tool. It will tell you if there’s anything wrong with the canonical tags on any of your pages. In case of a problem, you’ll see something like this:
Reason 5: A Recent Switch to HTTPS
In an era where online security and user trust are paramount, many website owners have made the necessary shift from HTTP to the more secure HTTPS protocol. While this change is undoubtedly a step in the right direction, it can temporarily impact your site’s indexing status. Google’s bots need time to adjust to the new secure protocol, which might result in a slight delay in indexing.
So, if you’ve recently migrated to HTTPS and noticed that your site isn’t appearing in Google’s search results as quickly as you’d hoped, don’t panic. This lag is often a normal part of the transition process.
However, there are steps you can take to expedite the indexing of your secure site.
Solution: configuration test and sitemap update
Firstly, ensure that your SSL certificate is correctly installed and configured. Next, update your website’s sitemap and resubmit it to Google Search Console, which signals to Google that changes have been made. Finally, monitor your site’s performance and indexing status over time, as it should gradually improve as Google’s bots adapt to the new protocol.
Get 111 Landing Page Examples—The Ultimate Guide for FREE
Reason 6: Your Site Is Too Big for Your Crawl Budget
If you’ve ever wondered why Google seems to miss some of your web pages, despite having what you believe is a well-structured and optimized website, the issue might be related to your crawl budget. The crawl budget value tells how many pages a search engine like Google can and will crawl on your site within a specified timeframe. For larger websites with thousands or even millions of pages, this budget can be limited.
A study from 2018 revealed that the crawl ratio (share of compliant pages in the website’s structure crawled by Google per month) accounts for only 49%. Average crawling by Google frequency equals 2.3 times (Botify, How does Google crawl the web?).
When your site exceeds its allocated crawl budget, search engine bots might not be able to explore all your pages thoroughly. As a result, some pages could go unindexed, causing potential SEO issues.
How to check if all your pages are currently not indexed? Simply use Google Search Console and their in-built page indexing report (or index coverage report):
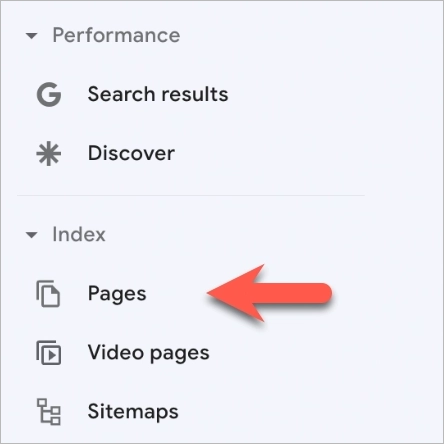
Solution: relevant pages prioritization
To address this challenge, consider the following steps:
Firstly, prioritize your most important pages and ensure they’re easily accessible from your site’s main navigation. By focusing on these key pages, you can increase the likelihood of them being crawled and indexed promptly.
Secondly, use the “robots.txt” file to guide search engine bots toward the sections of your site you want to prioritize and discourage crawling of less critical content.
Reason 7: Orphaned Pages
In the intricate maze of a website, sometimes pages get lost and left without a clear path for search engines to find them. These are what we call orphaned pages, and they pose a significant challenge to Google indexing.
Orphaned pages are those that lack internal links from other pages on your site, making them invisible to search engine crawlers. When Google’s bots cannot discover a page through links, they often don’t index it, leading to missed opportunities for visibility in search results.
The presence of 20% or more orphaned or poorly-linked pages on a website often indicates structural problems or issues related to failed migration (A. Smart, How to Fix Orphan Pages for SEO, 2022).
Remember, orphaned pages aren’t just missed opportunities for SEO; they can also lead to a fragmented user experience. So, cleaning up your site’s internal links not only benefits search engine indexing but also enhances your visitors’ navigation through your website.
Solution: internal links structure audit
To address this issue, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough audit of your website’s internal linking structure. Identify orphaned pages and find relevant, context-driven places within your site where you can include links to these pages. By interlinking your content strategically, you ensure that every page has a pathway for search engine bots to follow, increasing the chances of indexing and improved search visibility.
A simple way to detect orphaned pages is to check the entire site with crawling tools such as ScreamingFrog, or Sitebulb, and compare the URLs found with ones from the exported database file containing all the addresses on the site, those visible in Google Search Console or Google Analytics data. Addresses missing in crawlers reports are not indexed pages. To solve it, link to them from your other addresses appearing in Google index.
Reason 8: Hosting Issues
Your web hosting provider plays a vital role in the performance and accessibility of your website. However, hosting issues can become a roadblock to proper indexing by Google. Slow-loading pages, frequent downtime, or server errors can frustrate both visitors and search engine crawlers. When Googlebot encounters these issues, it may delay crawling, reduce the frequency of indexing, or even drop certain pages from the index.
Solution: reputable hosting provider and improving CDNs
To tackle hosting issues, start by choosing a reliable hosting provider that offers stable server performance, robust security measures, and quick response times. Regularly monitor your website’s uptime and page load speed using various online tools or services. If you notice any recurring problems, address them promptly with your hosting provider’s support team.
Choose hosting platforms ensuring a high security level (hacking protection, cyclic tests, etc.), regular updates, and advanced technical solutions (SSL certificates, reCAPTCHA, two-factor authentication 2FA, etc.). All of this is at your hand in Landingi.
Poor hosting may worsen page experience, which prevents 84% of customers from purchasing a product or service (G. Todorov, 117 Latest Web Hosting Stats 2023 [Facts and Trends], 2023).

Additionally, leverage Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to improve page load times, distribute server load, and enhance the overall user experience. CDNs can help mitigate issues related to slow-loading pages, particularly if you have a global audience.
Reason 9: “Crawled currently not indexed”
If your site was crawled but at the same time is currently not indexed, you may encounter such a message in your Google Search Console:
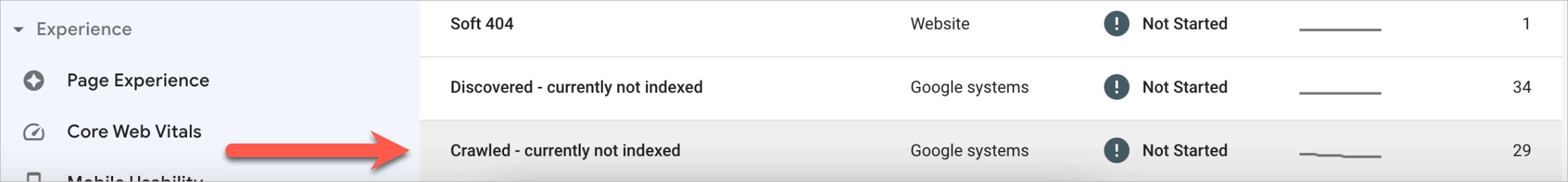
It may be one of the indexing errors, but in most cases one of the following reasons is involved:
Low-Quality Content: If your site contains low-quality or duplicated content, Google might choose not to index it. Google aims to provide valuable and unique content to its users, so pages with thin, irrelevant, or duplicate content may not make the cut.
Page Speed and Performance: Slow-loading pages or sites with poor performance may not be indexed as Google aims to provide a positive user experience. Optimize your site’s speed and performance.
Security Concerns: If your site has security issues, such as malware or hacked content, Google may not index it to protect users from potential harm. Regularly scan your site for security vulnerabilities.
Manual Actions: In cases of policy violations or spammy tactics, Google may take manual action against your site, resulting in non-indexing. Review Google Search Console for any manual actions against your site.
Solution: provide high-quality content, prioritize safety and performance issues
Ensure the content on your pages is high-quality and relevant to your audience. You may check it by analyzing users’ behavior on your sites via Google Analytics (e.g. time per visit and bounce rate stats may be valuable indicators in this matter) or – if they are landing pages – with Event Tracker.
Make website security a priority and regularly fine-tune its performance and speed. Perform regular audits and page-speed tests (at least with Google’s Lighthouse).
To Sum Up
The journey to effective Google indexing requires a keen understanding of potential stumbling blocks. The eight reasons we’ve discussed are often the culprits behind indexing woes. By diligently addressing each issue and adopting best SEO practices, you can not only secure your place in Google’s index but also stay ahead in the competitive online landscape.
With Landingi you can create your pages within the reliable infrastructure constantly developed to meet nowadays security and performance challenges. With a selection of powerful features (like no-code creating, hundreds of templates, AI text generation, etc.) and tools (akin to Event-Tracker) integrated into the platform, you will be able not just to create landing pages but at the same time make them effective marketing tools yielding tangible results: traffic, clicks, leads, and transactions.
Try it out at no charge!